Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Epidemiol Health > Volume 43; 2021 > Article
-
COVID-19: Original Article
The role of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies -
Mehmet Onur Kaya1
 , Esra Pamukçu2
, Esra Pamukçu2 , Burkay Yakar3
, Burkay Yakar3
-
Epidemiol Health 2021;43:e2021074.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4178/epih.e2021074
Published online: September 23, 2021
1Department of Biostatistics and Medical Informatics, Firat University School of Medicine, Elazığ, Turkey
2Department of Statistics, Faculty of Science, Fırat University, Elazığ, Turkey
3Department of Family Medicine, Firat University School of Medicine, Elazığ, Turkey
- Correspondence: Esra Pamukçu Department of Statistics, Faculty of Science, Fırat University, Elazığ 23119, Turkey E-mail: epamukcu@firat.edu.tr
©2021, Korean Society of Epidemiology
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
OBJECTIVES
- Although vaccination has started, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) poses a continuing threat to public health. Therefore, in addition to vaccination, the use of supplements to support the immune system may be important. The purpose of this study was to synthesize evidence on the possible effect of low serum vitamin D levels (25[OH]D<20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L) on COVID-19 infection and outcomes.
-
METHODS
- We searched Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect without any language restrictions for articles published between January 1 and December 15, 2020. We performed 3 meta-analyses (called vitamin D and COVID-19 infection meta-analysis [D-CIMA], vitamin D and COVID-19 severity meta-analysis [D-CSMA], and vitamin D and COV ID-19 mortality meta-analysis [D-CMMA] for COVID-19 infection, severity, and mortality, respectively) to combine odds ratio values according to laboratory measurement units for vitamin D and the measured serum 25(OH)D level.
-
RESULTS
- Twenty-one eligible studies were found to be relevant to the relationship between vitamin D and COVID-19 infection/outcomes (n=205,869). The D-CIMA meta-analysis showed that individuals with low serum vitamin D levels were 1.64 times (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.32 to 2.04; p<0.001) more likely to contract COVID-19. The D-CSMA meta-analysis showed that people with serum 25(OH)D levels below 20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L were 2.42 times (95% CI, 1.13 to 5.18; p=0.022) more likely to have severe COVID-19. The D-CMMA meta-analysis showed that low vitamin D levels had no effect on COVID-19 mortality (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 0.53 to 5.06, p=0.390).
-
CONCLUSIONS
- According to our results, vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of COVID-19 infection and the likelihood of severe disease. Therefore, we recommend vitamin D supplementation to prevent COVID-19 and its negative outcomes.
- Although coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is asymptomatic or has mild symptoms in the majority of the population, it may lead to death by causing serious clinical syndromes such as pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), myocarditis, microvascular thrombosis, and cytokine storm in some patients [1]. Therefore, there is a need to protect individuals from COVID-19, which is reported to have become more contagious as it has mutated, and to reduce the risk of severe disease and, consequently, the mortality rate. The COVID-19 vaccines that have been approved for emergency use have been a gleam of hope in the global struggle against COVID-19. However, the effects of vaccines on the immune system have not been clearly proven, and there have been some cases of severe COVID-19 cases, and even deaths, in patients who were fully vaccinated. As we have learned from similar viral infections, supplements such as vitamin D to support the immune system play an important role in addition to vaccination.
- Extensive research has explored the effects of vitamin D on the treatment and complications of COVID-19 and its potential contribution to the reduction of COVID-19 incidence. Vitamin D exerts antiviral activity and inhibits viral replication by stimulating the release of cathelicidin and defensin proteins in monocytes and macrophages [2,3]. Vitamin D plays an important role in preventing respiratory system infections due to its effects such as stimulating the chemotaxis of T-lymphocytes and clearing respiratory pathogens by inducing apoptosis and autophagy in the infected epithelium [4]. It has been reported that low T-lymphocyte levels were found in some COVID-19 patients with severe symptoms [5]. Since vitamin D supplementation increases the level of T-lymphocytes [6], this finding provides support for the hypothesis that vitamin D could be useful in the treatment of COVID-19.
- The severe progression of COVID-19 in some patients is one of the most important problems of the pandemic. Studies have pointed out an increased rate of thrombotic events and cytokine storm in severe COVID-19 patients. These events are responsible for fatal outcomes [7-9]. It is well known that vitamin D sufficiency reduces the risk of cytokine storm and regulates thrombotic pathways [10,11]. It has been reported that vitamin D sufficiency may attenuate the increased levels of inflammatory markers and cytokine storm during COVID-19 disease and that vitamin D deficiency (VDD) may be related to COVID-19 severity and mortality [12,13]. Consequently, the effect of VDD on COVID-19 infection and outcomes is topic that has attracted considerable interest.
- Most current studies about this subject have focused on the effect of VDD on COVID-19 infection, severity, and treatment, and findings on the relationship between VDD and COVID-19 mortality are limited. Therefore, as reported in the literature [13-15], more comprehensive clinical studies are still needed.
- Three meta-analyses of this issue have been published, one of which is a preprint article [16-18]. In these studies, we identified some problems such as inconsistent definitions of VDD (e.g., 25[OH]D < 20 or 12 ng/mL, < 50 or 30 nmol/L), the combination of different summary statistics (e.g., odds ratio [OR], risk ratio [RR], and hazard ratio [HR]), and a tendency to perform a meta-analysis of an individual study and give the results as if they were pooled results of a meta-analysis. In the Endocrine Society’s Practice Guidelines on Vitamin D, VDD is defined as a 25(OH)D level <20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L, vitamin D insufficiency as 21-29 ng/mL, and vitamin D sufficiency as at least 30 ng/mL for maximum musculoskeletal health [19]. This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis that establishes the association between COVID-19 infection/outcomes and VDD according to the common cut-off value (defining VDD as a 25[OH]D level < 20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L) proposed by advisory bodies. The purpose of this study was to synthesize evidence on the associations of VDD with COVID-19 infection, severity, and mortality and to provide an analytical contribution to the literature on the role of vitamin D supplementation in treatment and prevention protocols for COVID-19.
INTRODUCTION
- Throughout this systematic review and meta-analysis study, we followed the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines [20] (Supplementary Material 1).
- Search strategy
- We searched Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect without any language restriction and publication status limit. Our search keywords were “vitamin D” and “COVID-19,” “vitamin D” and “SARS-CoV-2,” and “vitamin D” and “coronavirus disease.” Articles that included the search keywords in their title and were published between January 1 and December 15, 2020 were chosen (Supplementary Material 2). We also screened the reference lists of other meta-analysis studies. Two independent researchers (MOK and EP) screened the titles, abstracts, and full-texts for inclusion in qualitative and quantitative analyses.
- Selection criteria
- The inclusion criteria for eligible studies were as follows: (1) cohort or case-control studies on the association between VDD and COVID-19 disease; (2) studies defining VDD according to the common definition (25[OH]D<20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L) as the exposure of interest; (3) studies in which the primary outcome was the risk of COVID-19 infection, severity, and mortality (given the number of cases as a cross-tabulated table). Studies were excluded if any of the following criteria were met: (1) non-human studies; (2) non-observational studies or observational studies without an analytical epidemiologic approach; (3) irrelevant exposure or outcome variables; (4) duplicate or unobtainable abstract/full-text; (5) studies that reported risk estimates (RR, OR, or HR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) without presenting the number of cases.
- Data extraction
- MOK and EP excluded reviews, replies, and letters. Research articles with inappropriate or inadequate results for the quantitative analysis were excluded. MOK and EP extracted the data using a standardized data format from studies that gave the number of cases according to vitamin D levels and COVID-19 infection/outcomes as a cross-tabulated table. We did not use the estimates of summary statistics presented in the studies. Any discrepancies were resolved by consensus. For the qualitative analysis, we created an electronic spreadsheet in which the following information was recorded: authors, location, region, study design, sample size, gender, population age, the definition of deficiency and insufficiency of vitamin D, the evaluated outcomes, and whether the study was included in the meta-analysis. Five studies [21-25] in the qualitative analysis were not included in the meta-analysis because they did not contain sufficient information for quantitative analysis.
- Statistical analysis
- We used the Mendeley Desktop version 1.19.4 (https://www.mendeley.com/) to remove duplicates and apply the inclusion criteria. Infection with COVID-19, severe COVID-19, and COVID-19 mortality were considered as COVID-19 outcomes in the meta-analyses. Serum levels of vitamin D are classified using definitions of VDD and vitamin D insufficiency according to advisory committees [26]. Vitamin D laboratory measurement units can be converted to each other as follows: 12 ng/mL=30 nmol/L, 20 ng/mL=50 nmol/L, and 30 ng/mL=75 nmol/L. Despite the existence of classifications and definitions of VDD cut-off values in the literature, some of the studies did not utilize these distinctions, as shown in Table 1 [27-47]. In order to create a subgroup according to a common cut-off value, we chose a serum 25(OH)D level of less than 20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L), as suggested in the 2011 Endocrine Society guideline [19], as indicative of deficiency.
- We extracted data from included studies that classified the number of cases according to serum vitamin D levels and COVID-19 infection/outcomes to calculate combined OR estimations. We did not use studies that presented vitamin D levels as mean or median values or presented summary statistics such as the OR, RR, HR, and incidence rate ratio (IRR) expressed without information on the number of cases. We created a subgroup of studies that used a cut-off of 25(OH)D< 20 ng/mL (or < 50 nmol/L). We also performed an overall meta-analysis without considering differences in the definition of serum 25(OH)D levels to compare the results.
- We examined the heterogeneity and the publication bias of the included studies using the Cochran Q test, the funnel plots, and the Egger test. Heterogeneity was detected in all groups according to the Cochran Q test and the level of heterogeneity was identified using the I2 index. Therefore, the Peto random-effect model was used to estimate combined OR values. We generated forest plots to show the detailed representation of all studies based on the OR effect size with 95% CIs. Moreover, since the Egger test detected publication bias in 1 of the meta-analyses conducted in this study, the trim-and-fill adjustment method was performed. All statistical analyses were done using RStudio version 1.2.5019 (https://docs.rstudio.com/) with R for Windows 4.0.3.
- Assesment of methodological quality
- The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) [48] (Supplementary Material 3) was used to assess the quality and risk of bias of studies. This tool contains 8 customized evaluation sheets with criteria divided into 3 groups: selection, comparability, and outcome. The case representativeness, research methodologies, and study outcomes were all reviewed on the assessment sheet. Different criteria were used to measure quality depending on different research designs. For the assessment of quality, a score of 3 stars or 4 stars in the selection domain and 1 star or 2 stars in the comparability domain and 2 stars or 3 stars in the exposure/outcome domain indicates good quality; a score of 2 stars in the selection domain and 1 star or 2 stars in the comparability domain and 2 stars or 3 stars in the exposure/outcome domain indicates fair quality; a score 0 or 1 star in the selection domain and 0 or 1 star in the comparability domain and 1 star or 2 stars in the exposure/outcome domain indicates poor quality.
- Ethics statement
- Additional ethical approval is not required since the meta-analysis studies used metadata from ethically approved research articles.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
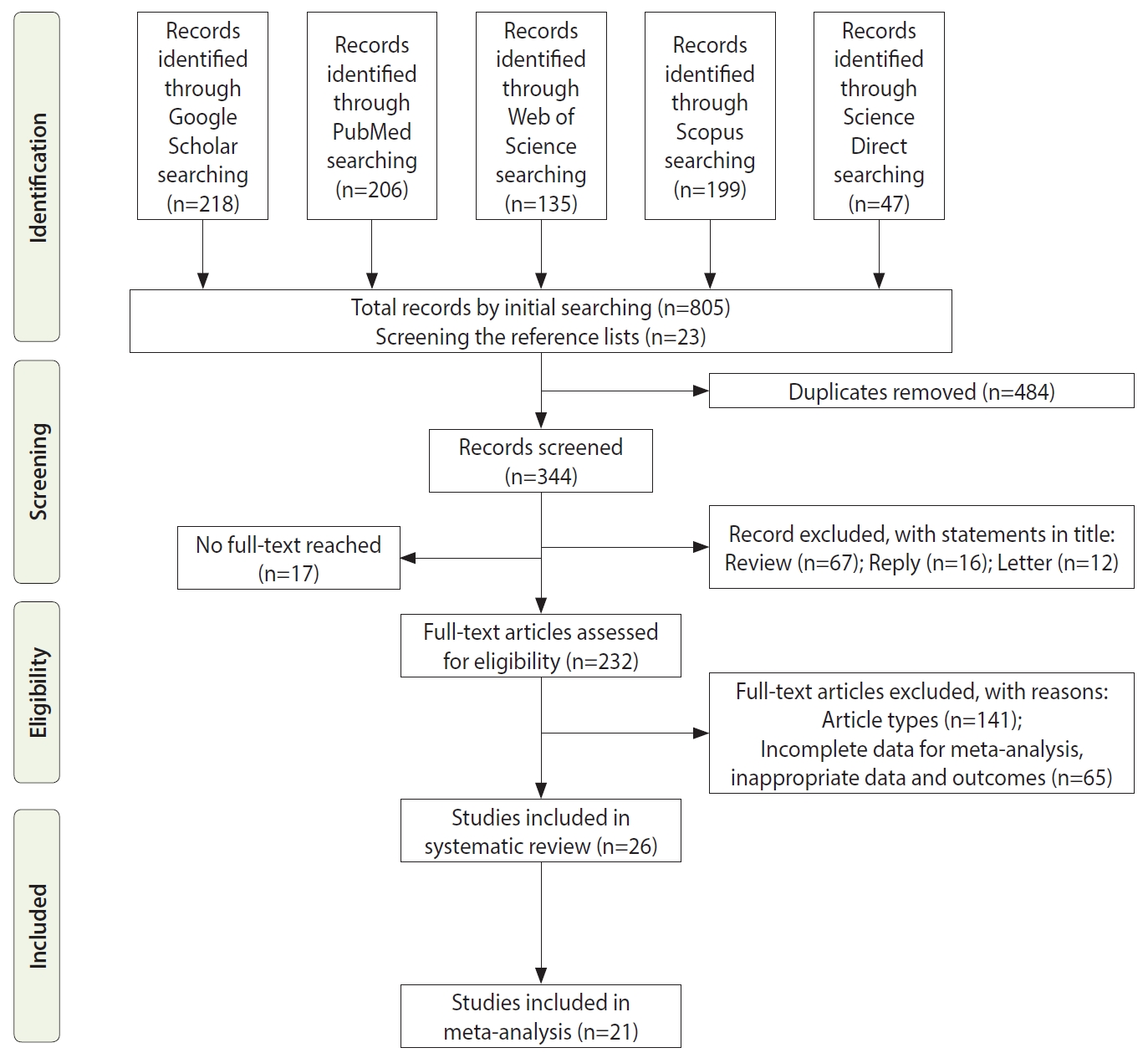
- The initial search yielded 805 articles from the search keywords and 23 articles from screening the reference lists. After the removal of duplicates and exclusion of studies on the basis of their abstracts or through examining their full text, 26 articles were eligible for our systematic review and 21 articles were eligible for the meta-analysis (Figure 1). Five studies were excluded from the meta-analysis because they did not report the data necessary to calculate ORs. Therefore, these studies were only included in the systematic review. The baseline characteristics of the studies are presented in Table 1. The studies were done in Europe (57.7%; 15 studies), Asia (30.8%; 8 studies), and America (11.5%; 3 studies). The total sample size of the 26 studies in the systematic review was 2,277,860. In the 25 studies that reported the gender distribution, the sample size was 1,935,974 (85.0%), of whom 896,444 (46.3%) were men. The summary statistics for the population age were presented in different ways such as mean± standard deviation (SD), and median (minimum-maximun or interquartile range [IQR]) in 15 studies. In 11 studies, the summary statistics were presented separately for each subgroup (case, control, etc.), but not for the overall population. Therefore, we could not obtain the mean or median values of population age from studies, but the light of the information that is available, it is clear that almost the entire population consisted of adults between the ages of 18 years and 85 years. Twelve studies measured 25(OH)D levels using units of ng/mL, 9 studies used nmol/L, 1 study used ng/dL, and 4 studies did not report it. VDD was defined as a 25(OH)D level < 10 ng/mL in 2 studies; < 12 ng/mL in 1 study; < 20 ng/mL in 9 studies; < 25 nmol/L in 3 studies; < 50 nmol/L in 3 studies. One study defined VDD as a 25(OH)D level < 20 ng/dL. In 1 of the studies, the cut-off value of the serum 25(OH)D level was reported as 34.4 nmol/L. This value was expressed as the cohort median, not as deficiency. Vitamin D insufficiency was defined as a 25(OH)D level <20 ng/mL in 1 study, <30 ng/mL in 7 studies, <50 nmol/L in 3 studies, and <75 nmol/L in 1 study.
- The COVID-19 outcomes evaluated in the studies were as follows: COVID-19 infection aloe in 8 studies, severity alone in 2 studies, infection and mortality in 2 studies, severity and mortality in 3 studies, infection and severity in 3 studies, infection and hospitalization in 1 study, hospitalization and severity in 1 study, hospitalization and mortality in 1 study. Among the studies that examined 3 outcomes, 3 studies reported COVID-19 infection, severity, and mortality; 1 study reported COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and severity; and 1 study reported COVID-19 hospitalization, severity, and mortality. Due to the limitations of the studies, we could not extract data on all the evaluated outcomes. Therefore, in some cases, the examined outcomes in meta-analyses and appropriate samples for the meta-analyses were less than the corresponding numbers in the original studies (Table 2).
- The NOS was used to assess the quality of the studies included in the meta-analyses [48] (Supplementary Material 3).
- The primary hypothesis was that there is a relationship between low vitamin D levels, defined as 25(OH)D < 20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L, and COVID-19 infection/outcomes. However, since the units of laboratory measurement and levels of measurement were different across the studies included in the meta-analyses, we also applied an overall meta-analysis that included all studies to show the degree to which these differences affected the findings. The results obtained from the overall meta-analyses are presented in the Supplementary Materials 4-7. We performed 6 meta-analyses, as follows:
- Vitamin D and COVID-19 infection meta-analysis (D-CIMA) for 25(OH)D < 20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L, with 8 included studies; vitamin D and COVID-19 infection meta-analysis (D-CIMAOverall) for all measurement units, with 11 included studies; vitamin D and COV ID-19 mortality meta-analysis (D-CSMA) for 25(OH)D <20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L, with 9 included studies; vitamin D and COVID-19 severity meta-analysis (D-CSMAOverall) for all measurement units, with 13 included studies); vitamin D and COVID-19 mortality meta-analysis (D-CMMA) for 25(OH)D <20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L, with 5 included studies; and vitamin D and COVID-19 mortality meta-analysis (D-CMMAOverall) for all measurement units, with 8 included studies.
- The sample sizes were: 202,561 and 203,962 in D-CIMA and D-CIMAOverall, 2,120 and 3,564 in D-CSMA and D-CSMAOverall, and 617 and 996 in D-CMMA and D-CMMAOverall, respectively. Since multiple outcomes were examined in the same sample in some studies included in the meta-analyses, there were overlapping samples. Considering these samples, the total sample size was 205,869. For the distribution of samples (Supplementary Material 8).
- In 1 study included in D-CIMA [33], we could not find the distribution of gender. Therefore, the number of samples for which the gender distribution could be determined was 19,615, of whom 8,750 (44.6%) were men. As mentioned before, the summary statistics for age were presented in different ways such as mean±SD and median (minimum-maximum or IQR). Therefore, we could not provide summary statistics about the age of the population from the studies, but in the light of available information, we can say that almost the entire population consisted of adults (18-85 years).
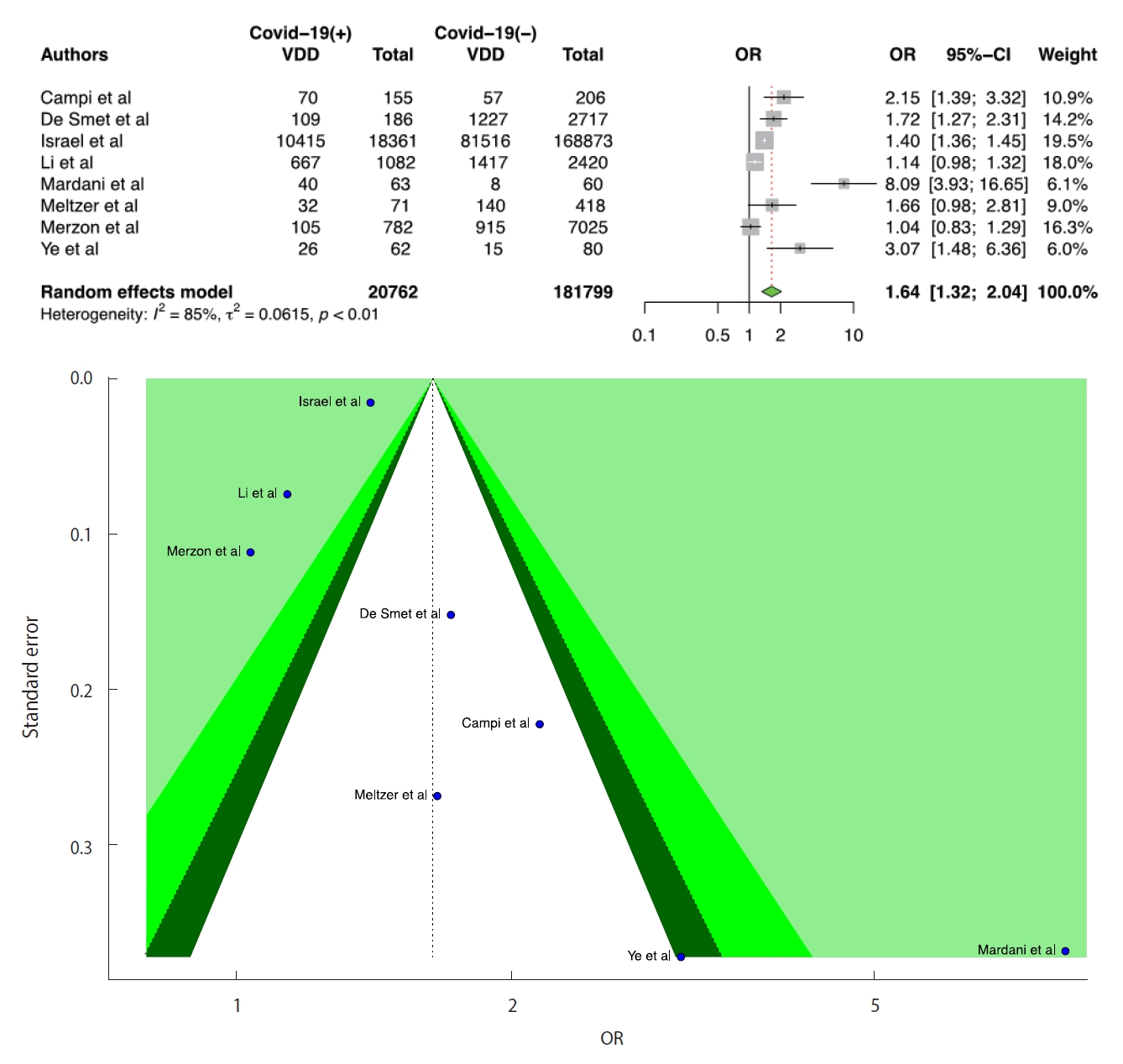
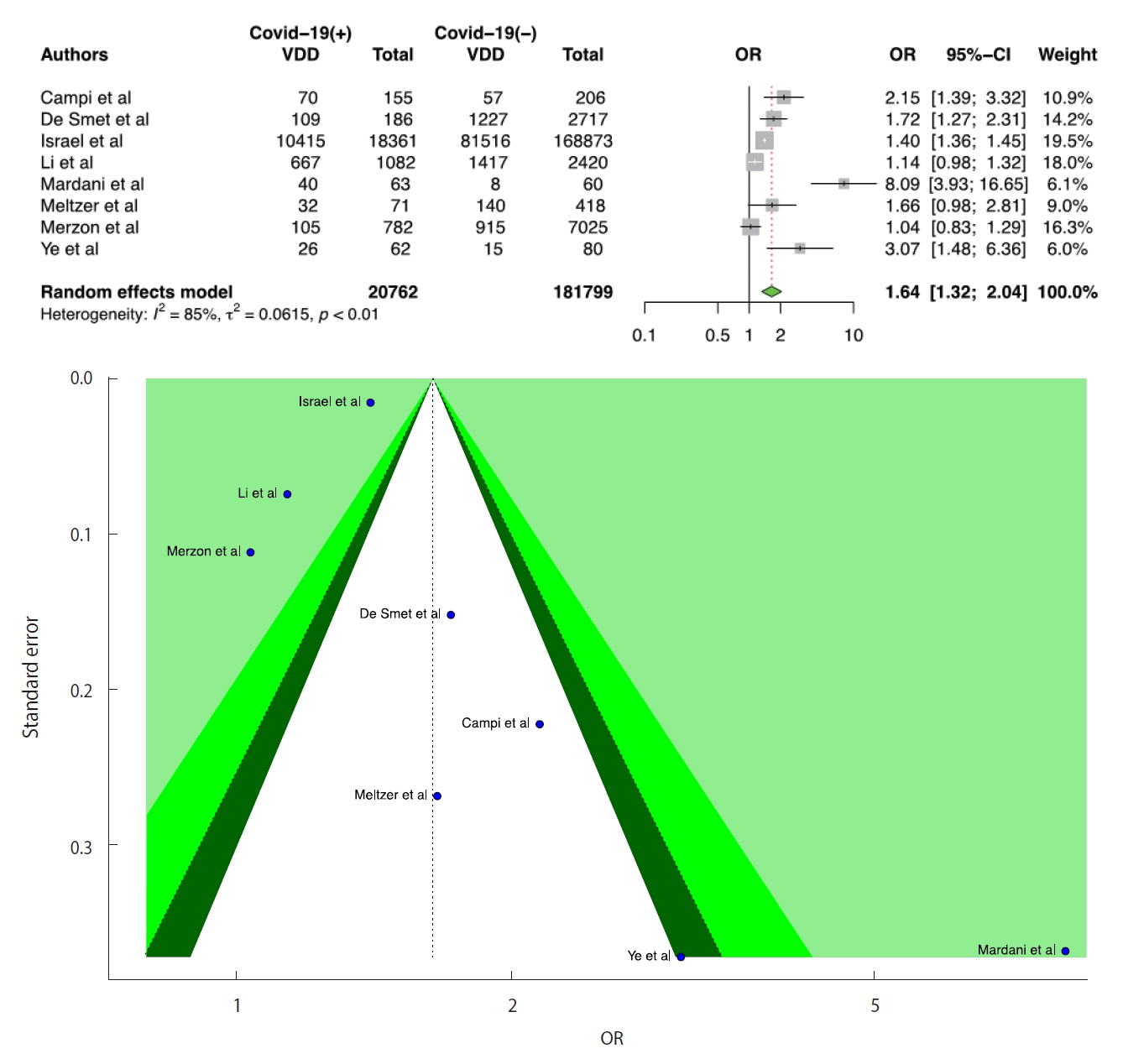
- We included 8 studies in the D-CIMA meta-analysis. All 8 studies reported that there was a significant positive relationship between VDD and the risk of infection. We also found that there was a significant positive relationship between COVID-19 infection and VDD (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.32 to 2.04; p<0.001). There was no publication bias in the 8 studies according to the Egger test (p=0.399). For heterogeneity, the following values were obtained: I2=85.4%; 95% CI, 73.2 to 92.1 and τ2=0.06; 95% CI, 0.05 to 1.02 (Cochran Q, p<0.001). We generated forest and funnel plots (Figure 2).
- We included 11 studies in the D-CIMAOverall meta-analysis. All studies except for 1 reported that there was a significant positive relationship between VDD and COVID-19 infection. According to D-CIMAOverall results, a low serum level of vitamin D was positively associated with COVID-19 infection (OR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.51 to 2.30; p<0.001). There was no publication bias in the 11 studies according to the Egger test (p=0.091). For heterogeneity, the following values were obtained: I2=87.0%; 95% CI, 78.7 to 92.1 and τ2=0.08; 95% CI, 0.06 to 0.76 (Cochran Q, p<0.001). We presented forest and funnel plots (Supplementary Material 4). Considering the D-CIMA and D-CIMAOverall results, we should note that the combined OR values are different. This is a remarkable finding that demonstrates the importance of distinction according to serum vitamin D level.
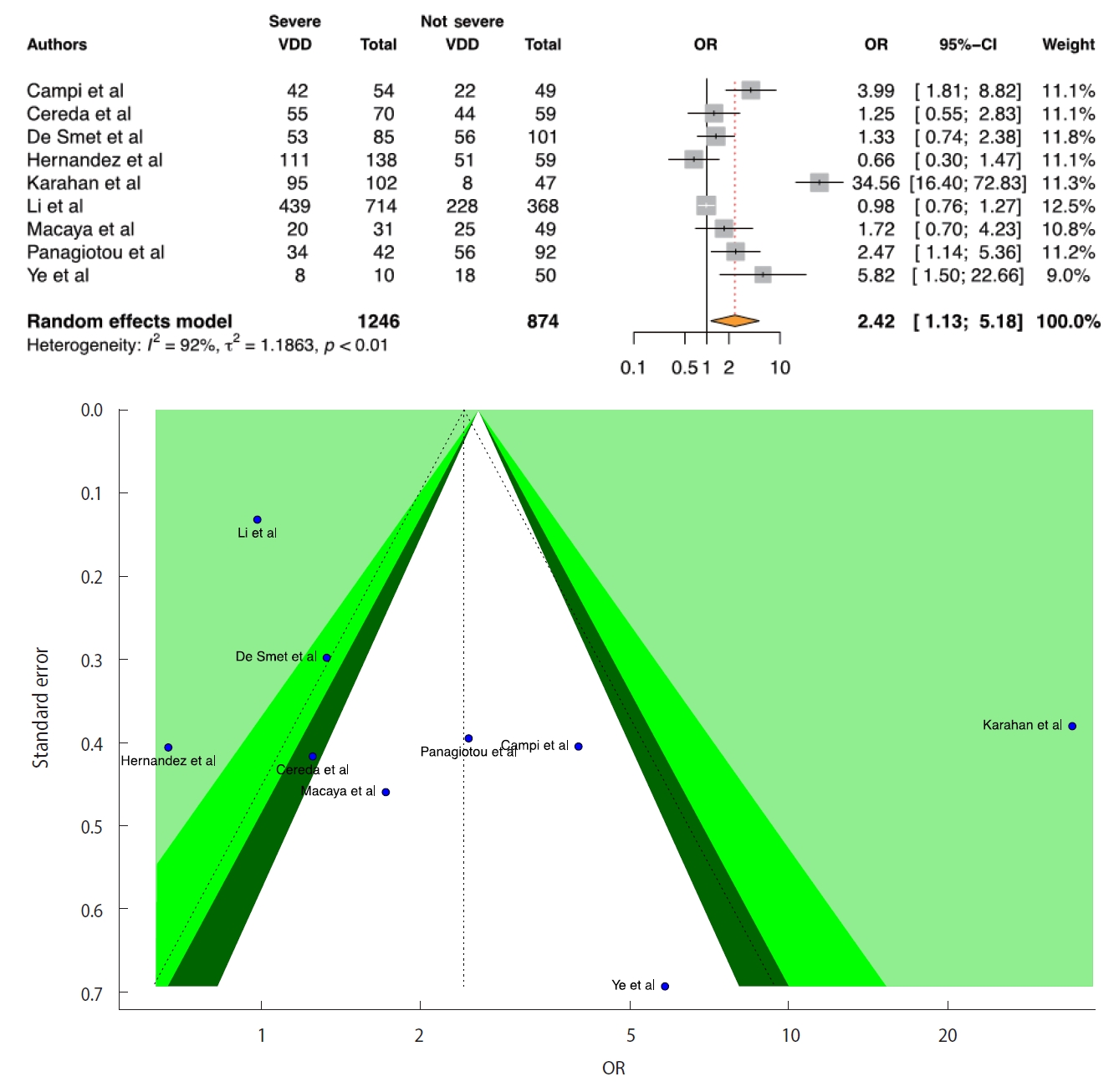
- We included 9 studies in the D-CSMA meta-analysis. All of the studies except for 1 [32] reported that there was a significant positive relationship between VDD and the risk of severe COVID-19. We obtained a significant positive relationship between COVID-19 severity and VDD (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.13 to 5.18; p=0.022). There was no publication bias in the 9 studies according to the Egger test (p=0.064). For heterogeneity, the following values were obtained: I2=91.5%; 95% CI, 86.1 to 94.8 and τ2=1.18; 95% CI, 0.47 to 5.29 (Cochran Q, p<0.001). We generated forest and funnel plots (Figure 3).
- We included 13 studies in the D-CSMAOverall meta-analysis. All studies except for 1 [32] reported that low serum levels of vitamin D were positively associated with COVID-19 severity. There was publication bias in the 13 studies according to the Egger test (p=0.017). Due to the presence of publication bias, we applied the trim-and-fill adjustment method. According to the adjusted results, there was no significant relationship between COVID-19 severity and low serum levels of vitamin D (OR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.71 to 2.17; p=0.445). This is also a remarkable finding that demonstrates the importance of distinguishing among serum vitamin D levels. The forest and funnel plots for the adjusted method are presented in Supplementary Material 5. For heterogeneity in the adjusted method, the following values were obtained: I2=92.8%; 95% CI, 90.2 to 94.7 and τ2=1.37; 95% CI, 0.88 to 3.98 (Cochran Q, p<0.001). Moreover, we also provided the overall results without applying the trim-and-fill adjustment to show that there is a difference in the results (Supplementary Material 6).
- Considering the D-CSMA and D-CSMAOverall results, we should note that conducting an analysis with all data leads to misleading results, such as finding that there is no relationship when one actually exists. This is also a remarkable finding that demonstrates the importance of distinguishing among serum vitamin D levels.
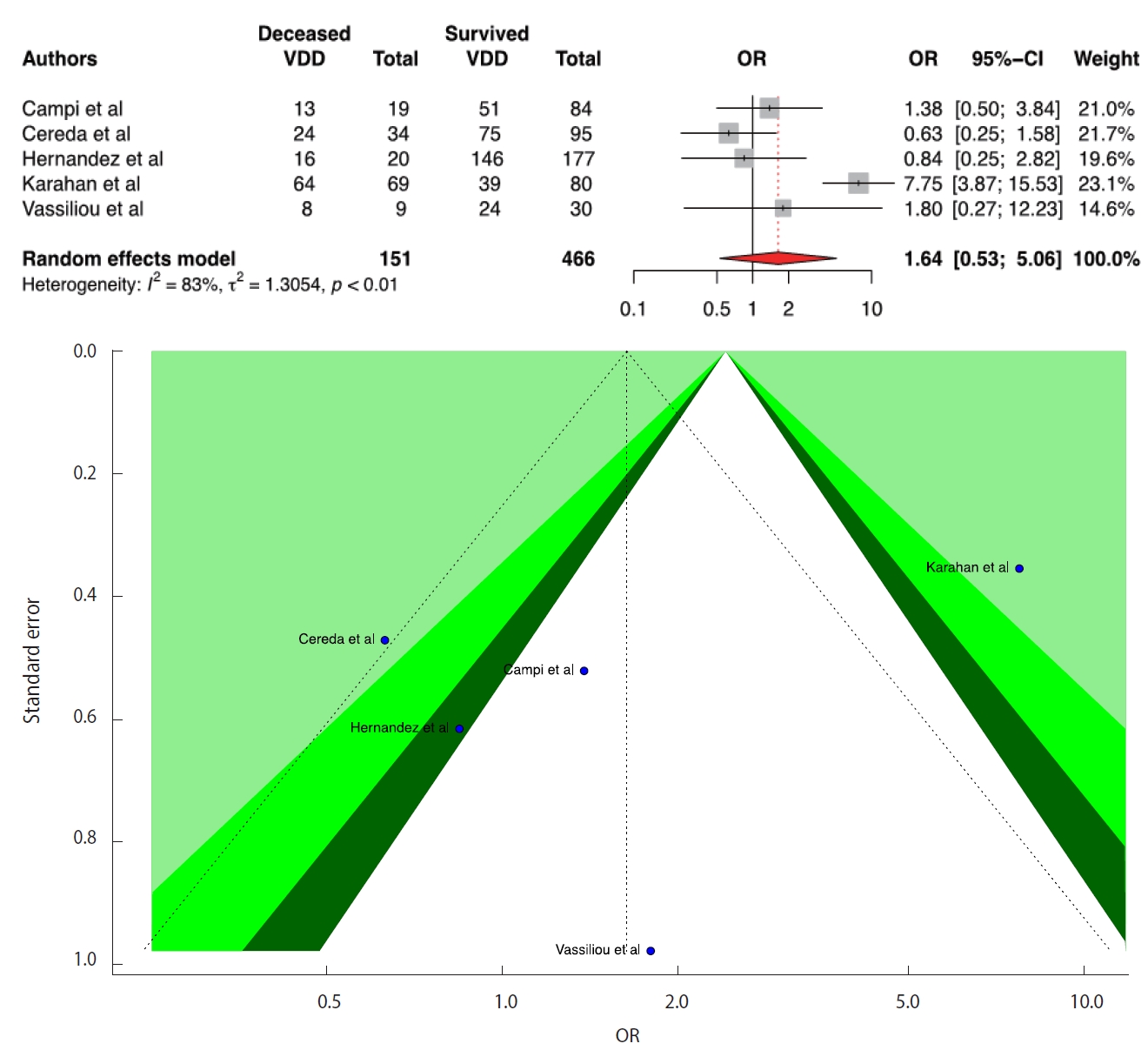
- We included 5 studies in the D-CMMA meta-analysis. Three studies reported a significant positive relationship between VDD and COVID-19 mortality. In contrast to the results reported in 3 studies, we found that there was no significant relationship between COVID-19 mortality and VDD (OR,1.64; 95% CI, 0.53 to 5.06; p=0.390). There was no publication bias in the 5 studies according to the Egger test (p=0.911). For heterogeneity, the following values were obtained: I2=82.6%; 95% CI, 60.0 to 92.4 and τ2=1.30; 95% CI, 0.12 to 10.51 (Cochran Q, p<0.001). Forest and funnel plots are presented in Figure 4.
- We included 8 studies in the D-CMMAOverall meta-analysis. While 4 studies of the 8 studies reported that low serum levels of vitamin D were positively associated with COVID-19 mortality, the rest of the studies reported that there was no significant relationship. We found that low serum levels of vitamin D were not associated with COVID-19 mortality (OR, 1.58; 95% CI, 0.76 to 3.27; p=0.211). There was no publication bias in the 8 studies according to the Egger test (p=0.909), and the following values were found for heterogeneity: I2=70.8%; 95% CI, 39.7 to 85.9 and τ2=0.71; 95% CI, 0.00 to 3.02 (Cochran Q, p=0.001). The forest and funnel plots are presented in Supplementary Material 7. All the results obtained from the meta-analyses are presented in Table 3.
RESULTS
- Although vaccination has started in many countries with vaccines that have been approved for emergency use, it seems that COVID-19 will continue to threaten public health for a long time. Therefore, there is a need to protect individuals from COVID-19, which is reported to have become more contagious due to mutations [49] and to reduce the risk of severe disease, consequently reducing the mortality rate. In addition to vaccination as a preventive measure against COVID-19, it has also been recommended to use supplements that strengthen the immune system [50,51]. From this point of view, the purpose of this study was to determine the possible effect of VDD on COVID-19 infection and outcomes due to its antiviral properties and to provide additional evidence in the literature. For this purpose, we conducted a systematic review of 26 studies and 3 meta-analyses of 21 studies, with careful attention paid to the laboratory measurement units for vitamin D and the measured serum 25(OH)D levels. We should emphasize that it is important to construct hypotheses based on a clear definition of VDD with serum 25(OH)D levels. However, studies have defined VDD using different serum 25(OH)D levels; for instance, a serum 25(OH)D level of 23 ng/mL would be defined as VDD in one study but as vitamin D insufficiency in another study. Therefore, analyzing findings in relation to VDD as defined in studies without accounting for how VDD was defined in terms of serum 25(OH)D levels may lead to misleading results. Our results have shown how important it is to make this distinction. Therefore, to the best of our knowledge, this meta-analysis study is the most comprehensive study to date in terms of the number of included studies, inclusion criteria, sample size, and well-defined hypotheses. However, our study has some limitations. In our study design, we did not include OR values that were presented in logistic regression models in the included studies to show the pure effect of VDD on the examined outcomes. Since the logistic models in the studies were established with different explanatory variables, the presented OR values cannot represent the same effect. We would have liked to provide evidence for comorbidities, treatment, and hospitalization through meta-analyses, but it was not possible to extract data suitable for our study design. The difficulties arising from the designs of the studies included in the meta-analyses during data extraction are presented in Table 3.
- According to the results from the D-CIMA meta-analysis, people with serum 25(OH)D levels below 20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L are 1.64 times more likely to be infected with COVID-19. COVID-19 infection then D-CSMA meta-analysis, we found that people with a serum 25(OH)D level below 20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L were 2.42 times more likely to have severe COVID-19. However, the DCMMA meta-analysis showed that low vitamin D levels had no effect on COVID-19 mortality. It is also important to discuss the results of the overall meta-analyses presented in the Supplementary Materials 4-7 along with our main findings. When 11 studies were combined without a distinction based on serum 25(OH)D levels in D-CIMAOverall, an OR of 1.86 was obtained (Supplementary Material 4). This is a misleading result that can be interpreted as showing that VDD will increase the risk of infection from COVID-19 to a greater extent. Similarly, when 13 studies were combined without discrimination according to serum 25(OH)D levels in D-CSMAOverall, no significant relationship was found between VDD and the risk of having severe COVID-19 (Supplementary Material 5). This result would cause the existing relationship to be ignored and the effect of vitamin D on preventing severity to be neglected. Although we could not find a significant relationship between VDD and mortality, we think that similar results also would be obtained for D-CMMA. However, due to the fact that the available data were limited, we could not provide sufficient evidence for the effect of vitamin D on mortality (Figure 4) (Supplementary Material 7).
- In our opinion, existing meta-analyses on the subject cannot provide reliable and sufficient evidence. Pereira et al. [16] performed a meta-analysis including 21 studies with 8,176 samples to examine the relationships of VDD with COVID-19 infection, severity, hospitalization, and mortality. They found that the relationship between VDD and COVID-19 infection is not significant (OR, 1.21; 95% CI, 0.83 to 1.60), but significant relationships between VDD and severity (OR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.30 to 2.09), hospitalization (OR, 1.81; 95% CI, 1.42 to 2.21), and mortality (OR, 1.82; 95% CI, 1.06 to 2.58). However, we identified some problems such as incorrect referencing, inconsistencies in the number of included studies throughout the text, the use of OR values in the meta-analyses that were not in the relevant studies, and incorrect presentation of the characteristics of the included studies. As an example, they included in the same meta-analysis Hastie et al. [23]’s article and corrigendum [52] of Hastie et al. [53]. Moreover, it is unclear how they obtained OR values from the corrigendum, where only a correction table about population characteristics was presented. In addition, although Hastie et al. [23] presented an IRR value for VDD < 25 nmol/L, Pereira et al. [16] used it as an OR value for VDD < 50 nmol/L. For more detail, we refer the reader to Pamukçu & Kaya [54]’s letter to the editor. Considering the other included studies, Meltzer et al. [41] and Darling et al. [22] presented their findings using RRs and ORs, respectively. It seems that Pereira et al. [16] combined different summary statistics such as IRRs, ORs, and RRs. Therefore, the findings obtained from that study are doubtful. Munshi et al. [17] conducted a meta-analysis study combining only 6 studies with a relatively small sample (n=376). They reported that patients with a poor prognosis had significantly lower serum levels of vitamin D than those with a good prognosis, with an adjusted standardized mean difference of -0.58 (95% Cl, -0.83 to -0.34; p<0.001). In addition, they presented a subgroup meta-analysis in which they examined differences in vitamin D according to regions. Here, it was determined that a subgroup was inappropriately formed from a single study. Chen et al. [18] conducted a meta-analysis including 6 studies with 377,265 samples to examine the relationships between VDD and COVID-19 infection, hospitalization, and mortality. They found a significant association for COVID-19 infection (OR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.09 to 1.97) and hospitalization (OR, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.22 to 2.74), while they did not find a meaningful relationship for mortality (OR, 2.73; 95% CI, 0.27 to 27.61). Although subgroup analyses were performed according to serum 25(OH)D levels < 20 ng/mL and < 30 ng/mL, the results were given in the overall estimate. The problem of the subgroup analysis being performed with a single study was also identified here. When we consider our findings together with the results obtained from these studies, we can say that we put forth more credible evidence regarding the relationship between VDD and COVID-19 infection and severity.
- As we present in the Results section, our findings support previous results in the literature, according to which vitamin D supplementation has a protective effect against acute respiratory infections [55]. It has been reported that antigen-presenting cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells play a role in the synthesis of the active form of vitamin D and that macrophages and dendritic cells can be affected by vitamin D. Studies have reported that active vitamin D (1,25[OH]2D) synthesis is reduced during VDD, so the immune response, including innate immune function, will be impaired. In addition, vitamin D shows antimicrobial and antiviral activity by increasing the expression of cathelicidin/defensin. Cathelicidin and defensin contributes to host defense by stimulating the expression of antiviral cytokines and chemokines involved in the recruitment of monocytes/macrophages, natural killer cells, neutrophils, and T cells. Cellular production of cathelcidin and defensin depends on the vitamin D receptor and CYP27B1, the expression of which is enhanced following interactions of pathogens with membrane pattern recognition receptors, such as toll-like receptor and toll-like receptor 2. The above-mentioned mechanism explains the role of vitamin D in combating respiratory viruses [56]. In the early stage of infection, it limits viral entry and replication by increasing cathelicidin and defensin expression in the respiratory epithelium [57]. In COVID-19, pneumonia and ARDS have been identified as responsible for severe disease. Many studies have reported the protective effects of vitamin D against pneumonia, cytokine hyperproduction, and many conditions associated with ARDS [58,59]. It has also been reported that VDD is directly associated with the risk of acute respiratory failure [60,61]. In a rat study, it was reported that vitamin D supplementation reduced lung damage and attenuated disease severity in rats with ARDS [62]. Although sufficient data have not been found for COVID-19, vitamin D has recently been recommended as a drug to treat lung damage in pneumonia caused by influenza A virus [63]. In light of the evidence we have obtained, vitamin D supplementation can be recommended to reduce the severity of COVID-19 disease.
- The fact that COVID-19 mortality rates differ between countries and that mortality rates are lower in the Southern Hemisphere has attracted attention to the relationship between VDD and death. In a study conducted in European countries, which are located in the Northern Hemisphere and do not have sufficient sunlight in winter, it has been reported that average vitamin D levels are associated with mortality, especially in countries with a high prevalence of VDD such as Italy and Spain where the mortality due to COVID-19 has been high [64]. Although it has been found that benefiting from sunlight reduces influenza infection and related mortality, no studies in the literature have elucidated the effect of vitamin D supplementation and seasonal changes on mortality associated with COVID-19 [51,65]. The cytokine storm, which causes hyperinflammation and tissue damage, has been found to be responsible for the mortality associated with COVID-19 [66]. In the literature, it has been emphasized that vitamin D can be an important agent in preventing cytokine storm and ARDS. Based on this information, it is reasonable to hypothesize that vitamin D can reduce the mortality rate due to COVID-19. However, the current literature could not provide adequate data to support this hypothesis in our meta-analysis. We should note that large-scale and multi-center randomized controlled studies are still needed to determine the effectiveness of vitamin D as a treatment to reduce disease severity and mortality.
- CONCLUSION
- Despite the fact that the vaccination has started in many countries, it appears that COVID-19 will continue to threaten public health for a long time. Hence, in addition to the vaccine, the usage of immune-supporting supplements may be beneficial. The main purpose of this study was to synthesize evidence on the possible effect of low serum vitamin D levels (25[OH]D < 20 ng/mL or 50 nmol/L) on COVID-19 infection and outcomes. According to our results, VDD may increase the risk of COVID-19 infection and the potential for severe disease. Therefore, vitamin D supplementation may be added to prevention and treatment protocols for COVID-19. It should be noted that current measures to reduce transmission, such as frequent hand washing, wearing a mask, physical separation, air circulation, and avoiding crowded locations or enclosed spaces, continue to work against new varieties by limiting viral transmission and thereby reducing the virus’s ability to mutate. Vaccines are a vital tool in the fight against COVID-19, and employing extant tools will have significant public health and lifesaving benefits.
DISCUSSION
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare for this study.
-
Funding
None.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: MOK, EP, BY. Data curation: MOK, EP. Formal analysis: MOK, EP. Funding acquisition: None. Methodology: MOK, EP, BY. Visualization: MOK, EP. Writing – original draft: MOK, EP. Writing – review & editing: MOK, EP, BY.
NOTES
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
| Study | Location | Region | Study design | Sample size | Gender (men), n (%) | Population age mean±SD or median [Min-Max or IQR] | The definition of VDD and/or VDIS | Outcomes evaluated in the study | Included in the meta-analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdollahi et al. [27] | Iran | Asia | Case-control | 402 | 132 (32.8) | 47.1±15.3 | VDD<10 ng/mL | I | Yes |
| VDIS<30 ng/mL | |||||||||
| Baktash et al. [28] | UK | Europe | Cross-sectional | 105 | 57 (54.2) | 81 [65-102] | VDD<30 nmol/L | I-M | Yes |
| Campi et al. [29] | Italy | Europe | Cohort | 361 | 243 (67.0) | 66 [54–78] | VDD<50 nmol/L | I-S-M | Yes |
| Cereda et al. [30] | Italy | Europe | Cohort | 129 | 70 (54.3) | 77 [65–85] | VDD<20 ng/mL | S-M | Yes |
| VDIS<30 ng/mL | |||||||||
| D’Avolio et al. [21] | Switzerland | Europe | Case-control | 1,484 | 682 (45.9) | NR | NR | I | No |
| Darling et al. [22] | UK | Europe | Case-control | 1,303 | 713 (54.7) | 57.7±8.7 | NR | I | No |
| De Smet et al. [31] | Belgium | Europe | Cross-sectional | 2,903 | 1,108 (38.1) | NR | VDD<20 ng/mL | I-S | Yes |
| Hastie et al. [23] | UK | Europe | Cohort | 341,484 | NR | NR | VDD<25 nmol/L | I-M | No |
| VDIS<50 nmol/L | |||||||||
| Hernández et al. [32] | Spain | Europe | Case-control | 413 | 253 (61.2) | NR | VDD<20 ng/mL | I-S-M | Yes |
| Im et al. [24] | Korea | Asia | Case-control | 200 | 84 (42.0) | 52.3±20.3 | VDD<20 ng/dL | I-S | No |
| Israel et al. [33] | Israel | Asia | Case-control | 576,455 | 271,601 (47.1) | NR | VDD<50 nmol/L | I | Yes |
| Karahan and KatKat [34] | Turkey | Europe | Cross-sectional | 149 | 81 (54.3) | 63.5±15.3 | VDD<20 ng/mL | S-M | Yes |
| VDIS<30 ng/mL | |||||||||
| Katz et al. [25] | USA | America | Case-control | 987,849 | 455,458 (46.1) | NR | NR | I | No |
| Li et al. [35] | UK | Europe | Case-control | 353,299 | 161,298 (45.6) | 67.7±8.1 | VDD<25 nmol/L | I-H-S | Yes |
| VDIS<50 nmol/L | |||||||||
| Livingston et al. [36] | UK | Europe | Cohort | 104 | 39 (37.5) | 68.5±18.3 | VDSL<34.4 nmol/L | I | Yes |
| Luo et al. [37] | China | Asia | Cross-sectional | 895 | 405 (45.2) | NR | VDD<30 nmol/L | I-S-M | Yes |
| Macaya et al. [38] | Spain | Europe | Cohort | 80 | 35 (43.7) | NR | VDD<20 ng/mL | S | Yes |
| Maghbooli et al. [39] | Iran | Asia | Cross-sectional | 235 | 144 (61.3) | 58.7±15.2 | VDD<20 ng/mL | H-S-M | Yes |
| VDIS<30 ng/mL | |||||||||
| Mardani et al. [40] | Iran | Asia | Cross-sectional | 123 | 65 (52.8) | 42.1±14,9 | VDD<10 ng/mL | I | Yes |
| VDIS<30 ng/mL | |||||||||
| Meltzer et al. [41] | USA | America | Case-control | 489 | 123 (25.0) | 49.2±18.4 | VDD<20 ng/mL | I | Yes |
| Mendy et al. [42] | USA | America | Cohort | 689 | 365 (53.0) | 49.5 [35.2–67.5] | NR | H-S | Yes |
| Merzon et al. [43] | Israel | Asia | Case-control | 7,807 | 3,234 (41.4) | 41.4±NR | VDD<20 ng/mL | I-H | Yes |
| VDIS<30 ng/mL | |||||||||
| Panagiotou et al. [44] | UK | Europe | Cohort | 134 | 73 (54.4) | 68.7±14.0 | VDD<25 nmol/L | S | Yes |
| VDIS<50 nmol/L | |||||||||
| Radujkovic et al. [45] | Germany | Europe | Cohort | 185 | 95 (51.0) | 60 [49–70] | VDD<12 ng/mL | S-M | Yes |
| VDIS<20 ng/mL | |||||||||
| Vasiliou et al. [46] | Greece | Europe | Cohort | 39 | 31 (79.4) | 61.5±13.2 | VDD<20 ng/mL | H-M | Yes |
| VDIS<30 ng/mL | |||||||||
| Ye et al. [47] | China | Asia | Case-control | 142 | 55 (38.7) | NR [0.1-85] | VDD<50 nmol/L | I-S | Yes |
| VDIS<75 nmol/L |
| Study | Sample size in the study |
Sample size included in meta-analyses |
Outcomes evaluated in the study | Outcomes evaluated in the meta-analyses | Findings in the study1 | Limitations in extracting data | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-CIMA | D-CSMA | D-CMMA | ||||||
| Abdollahi et al. [27] | 402 | 402 | – | – | I | I | I(+) | VDD was defined as <10 ng/mL, but the sample distribution for VDD was not suitable for statistical analysis; A statistical comparison was made for VDIS <30 ng/mL; Therefore, the data belonging to VDIS were included in the meta-analysis, and the measurement unit was assigned as “other” |
| Baktash et al. [28] | 105 | – | – | 70 | I-M | M | I(+); M(-) | There was uncertainty in the definition of comparison groups for COVID-19 infection; We sent an email to the corresponding author, but we did not receive a reply; Therefore, COVID-19 infection data were not included in the D-CIMA |
| Campi et al. [29] | 361 | 361 | 103 | 103 | I-S-M | I-S-M | I(+); S(+); M(+) | There was no limitation in data extraction |
| Cereda et al. [30] | 129 | – | 129 | 129 | S-M | S-M | S(+); M(+) | The clinical outcomes were severe pneumonia, admission to the ICU, and in-hospital mortality; The ICU admission data were not appropriate for statistical analysis (0 observed cases); Therefore, we extracted data from severe pneumonia for the analysis of severity |
| D’Avolio et al. [21] | 1,484 | – | – | – | I | – | I(+) | The definition of VDD was not available; There was no adequate information dealing with descriptive statistics; VDD was presented as median (IQR) and the findings were presented graphically; Since we extracted the data based on the number of cases, we did not include it in the meta-analysis In the study, the date of the data received from UK Biobank for the COVID-19 (-) control group was long ago; There was no VDD definition and they used quartile values of VDD; Since we extracted the data based on the number of cases, we did not include it in the meta-analysis |
| Darling et al. [22] | 1,303 | – | – | – | I | – | I(-) | In the study, the date of the data received from UK Biobank for the COVID-19 (-) control group was long ago; There was no VDD definition and they used quartile values of VDD; Since we extracted the data based on the number of cases, we did not include it in the meta-analysis |
| De Smet et al. [31] | 2,903 | 2,903 | 186 | – | I-S | I-S | I(+); S(+) | In the study, chest CT was performed for all COVID-19 patients to determine the disease stage; They classified the patients as stage 1 (early stage), stage 2 (progressive stage), and stage 3 (peak stage); We chose severe cases from stage 3 and non-severe cases from stage 1-2 |
| Hastie et al. [23] | 341,484 | – | – | – | I-M | – | I(-); M(-) | There was no adequate information dealing with descriptive statistics; The findings were presented by using HR and IRR values; Since we extracted the data based on the number of cases, we did not include it in the meta-analysis |
| Hernández et al. [32] | 413 | – | 197 | 197 | I-S-M | S-M | I(+); S(-); M(-) | For COVID-19 infection, VDD was presented as mean (±SD); Since the number of cases was not reported, we could not include it in D-CIMA |
| Im et al. [24] | 200 | – | – | – | I-S | – | I(+); S(+) | In the study, the unit of ng/dL was used for laboratory measurements of serum 25(OH)D levels, and VDD was defined as 25(OH)D<20 ng/dL; We converted 20 ng/dL to 0.2 ng/mL; Since we thought there was an inconsistency, we could not include these data in the meta analyses |
| Israel et al. [33] | 576,455 | 187,234 | – | – | I | I | I(+) | Age matching was performed between the case and control groups, but single summary statistics for the population were not presented |
| Karahan and Katkat [34] | 149 | – | 149 | 149 | S-M | S-M | S(+); M(+) | There was no limitation in data extraction |
| Katz et al. [25] | 987,849 | – | – | – | I | – | I(+) | There was no adequate information dealing with descriptive statistics; The findings were presented as ORs; Since we extracted the data based on the number of cases, we did not include it in the meta-analysis |
| Li et al. [35] | 353,299 | 3,502 | 1,082 | – | I-H-S | I-S | I(+); H(+); S(+) | This study defined hospitalization as one record of origin (whether the patient s tested positive or not); In the study, hospitalized, confirmed, and severe COVID-19 cases were compared with community controls; We think that this study design is inappropriate; For this reason, we extracted data on infections from patients who presented to the hospital with suspected COVID-19 and confirmed COVID-19, and for the severity from patients with confirmed and severe COVID-19 |
| Livingston et al. [36] | 104 | 104 | – | – | I | I | I(-) | The definition of VDD was not available; Statistical comparisons were performed for 25(OH)D <34.4 nmol/L; Therefore, the data belonging to this distinction were included in the meta-analysis, and the measurement unit was assigned as “other” |
| Luo et al. [37] | 895 | 895 | 335 | 74 | I-S-M | I-S-M | I(+); S(+); M(-) | There was no limitation in data extraction |
| Macaya et al. [38] | 80 | – | 80 | S | S | S(+) | There was no limitation in data extraction | |
| Maghbooli et al. [39] | 235 | – | 235 | 235 | H-S-M | S-M | H(+); S(+); M(+) | There was no limitation in data extraction; Although the authors defined VDD as 25(OH)D<20 ng/mL, the dataset that could be extracted from the article belonged to the category of 25(OH)D<30 ng/mL; Therefore, it was included in the overall analysis |
| Mardani et al. [40] | 123 | 123 | – | – | I | I | I(+) | We extracted data from their supplementary file according to 25(OH)D<20 ng/mL |
| Meltzer et al. [41] | 489 | 489 | – | – | I | I | I(+) | There was no limitation in data extraction |
| Mendy et al. [42] | 689 | – | 689 | – | H-S | S | H(+); S(+) | The definition of VDD was not available; Therefore, the measurement unit was assigned as “other” in the D-CSMA |
| Merzon et al. [43] | 7,807 | 7,807 | – | – | I-H | I | I(+); H(+) | There was no limitation in data extraction |
| Panagiotou et al. [44] | 134 | – | 134 | – | S | S | S(+) | The authors classified the patients as admitted to the ITU and non-ITU wards; |
| When we extracted data, we chose patients admitted to non-ITU wards as non-severe and those admitted to ITU wards as severe; A statistical comparison was made for VDIS <50 nmol/L; Therefore, the data belong to VDIS were included in the D-CSMA | ||||||||
| Radujkovic et al. [45] | 185 | – | 185 | – | S-M | S | S(+); M(+) | The authors classified patients as inpatients and outpatients; When we extracted data, we chose the outpatients as non-severe and the inpatients as severe according to their definition |
| Vassiliou et al. [46] | 39 | – | – | 39 | H-M | M | H(-); M(-) | There was no limitation in data extraction |
| Ye et al. [47] | 142 | 142 | 60 | – | I-S | I-S | I(+); S(+) | There was no limitation in data extraction |
| Total | 2,277,860 | 203,962 | 3,564 | 996 | ||||
COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; D-CIMA, vitamin D and COVID-19 infection meta-analysis; D-CSMA, vitamin D and COVID-19 severity meta-analysis; D-CMMA, vitamin D and COVID-19 mortality meta-analysis; I, COVID-19 infection; S, severity; M, mortality; H, hospitalization; VDD, vitamin D deficiency; ICU, intensive care unit; IQR, interquartile range; CT, computed tomography; HR, hazard ratio; IRR, incidence rate ratio; SD, standard deviation; OR, odds ratio; ITU, intensive therapy unit; VDIS, vitamin D insufficiency.
1 (+), indicates that the association of low levels of vitamin D and I, S, M and H was statistically significant; (-) indicates that the association of low levels of vitamin D and I, S, M and H was not statistically significant.
| Meta-analyses |
Publication bias |
Heterogeneity |
Quantifying heterogeneity |
Findings of meta-analyses |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egger test (p-value) | Cochran Q test (p-value) | I2 (95% CI), %/τ2 (95% CI) |
Peto random-effect model |
||
| OR (95% CI) | p-value | ||||
| D-CIMA for serum 25(OH)D levels <20 ng/mL and 50 nmol/L | 0.399 | <0.001 | 85.4 (73.2, 92.1)/0.06 (0.05, 1.02) | 1.64 (1.32, 2.04) | <0.001 |
| D-CIMAOverall for serum 25(OH)D levels with all different measurement units | 0.091 | <0.001 | 87.0 (78.7, 92.1)/0.08 (0.06, 0.76) | 1.86 (1.51, 2.30) | <0.001 |
| D-CSMA for serum 25(OH)D levels <20 ng/mL and 50 nmol/L | 0.064 | <0.001 | 91.5 (86.1, 94.8)/1.18 (0.47. 5.29) | 2.42 (1.13, 5.17) | 0.022 |
| D-CSMAOverall for serum 25(OH)D levels with all different measurement units | 0.017 | <0.001 | 92.8 (90.2, 94.7)1/1.37 (0.88, 3.98)1 | 1.24 (0.71, 2.17)1 | 0.445 |
| D-CMMA for serum 25(OH)D levels <20 ng/mL and 50 nmol/L | 0.911 | <0.001 | 82.6 (60.1, 92.4)/1.30 (0.12, 10.51) | 1.64 (0.53, 5.06) | 0.390 |
| D-CMMAOverall for serum 25(OH)D levels with all different measurement units | 0.909 | 0.001 | 70.8 (39.7, 85.9)/0.71 (0.00, 3.02) | 1.58 (0.76, 3.27) | 0.211 |
- 1. Cascella M, Rajnik M, Aleem A, Dulebohn S, Di Napoli R. Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19); 2021 [cited 2021 Oct 1]. Available from: https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/52171.
- 2. White JH. Vitamin D metabolism and signaling in the immune system. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2012;13:21-29.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Gombart AF, Borregaard N, Koeffler HP. Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly up-regulated in myeloid cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. FASEB J 2005;19:1067-1077.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Adams JS, Ren S, Liu PT, Chun RF, Lagishetty V, Gombart AF, et al. Vitamin D-directed rheostatic regulation of monocyte antibacterial responses. J Immunol 2009;182:4289-4295.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Chen G, Wu D, Guo W, Cao Y, Huang D, Wang H, et al. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J Clin Invest 2020;130:2620-2629.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Cantorna MT, Snyder L, Lin YD, Yang L. Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D regulation of T cells. Nutrients 2015;7:3011-3021.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Franchini M, Marano G, Cruciani M, Mengoli C, Pati I, Masiello F, et al. COVID-19-associated coagulopathy. Diagnosis (Berl) 2020;7:357-363.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Hu B, Huang S, Yin L. The cytokine storm and COVID-19. J Med Virol 2021;93:250-256.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Wang Y, Zhou Y, Yang Z, Xia D, Hu Y, Geng S. Clinical characteristics of patients with severe pneumonia caused by the SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Respiration 2020;99:649-657.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Alhassan Mohammed H, Mirshafiey A, Vahedi H, Hemmasi G, Moussavi Nasl Khameneh A, Parastouei K, et al. Immunoregulation of inflammatory and inhibitory cytokines by vitamin D3 in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Scand J Immunol 2017;85:386-394.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Daneshkhah A, Agrawal V, Eshein A, Subramanian H, Roy HK, Backman V. Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients. Aging Clin Exp Res 2020;32:2141-2158.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Mohammad S, Mishra A, Ashraf MZ. Emerging role of vitamin D and its associated molecules in pathways related to pathogenesis of thrombosis. Biomolecules 2019;9:649.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Weir EK, Thenappan T, Bhargava M, Chen Y. Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19? Clin Med (Lond) 2020;20:e107-e108.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Zemb P, Bergman P, Camargo CA Jr, Cavalier E, Cormier C, Courbebaisse M, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and the COVID-19 pandemic. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 2020;22:133-134.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Grant WB, Lahore H, McDonnell SL, Baggerly CA, French CB, Aliano JL, et al. Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths. Nutrients 2020;12:988.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Pereira M, Dantas Damascena A, Galvão Azevedo LM, de Almeida Oliveira T, da Mota Santana J. Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2020;Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090.Article
- 17. Munshi R, Hussein MH, Toraih EA, Elshazli RM, Jardak C, Sultana N, et al. Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol 2021;93:733-740.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Chen J, Xie L, Yuan P, Ma J, Yu P, Zheng C, et al. Low serum vitamin D level and COVID-19 infection and outcomes, a multivariate meta-analysis. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 [cited 2020 Dec 20]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.24.20218974.Article
- 19. Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:1911-1930.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 2009;6:e1000097.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. D’Avolio A, Avataneo V, Manca A, Cusato J, De Nicolò A, Lucchini R, et al. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2. Nutrients 2020;12:1359.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Darling A, Ahmadi K, Ward K, Harvey N, Alves A, Dunn-Walters D, et al. Vitamin D concentration, body mass index, ethnicity and SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19: initial analysis of the first- reported UK Biobank Cohort positive cases (n 1474) compared with negative controls (n 4643). Proc Nutr Soc 2021;80:E17.Article
- 23. Hastie CE, Pell JP, Sattar N. Vitamin D and COVID-19 infection and mortality in UK Biobank. Eur J Nutr 2021;60:545-548.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Im JH, Je YS, Baek J, Chung MH, Kwon HY, Lee JS. Nutritional status of patients with COVID-19. Int J Infect Dis 2020;100:390-393.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Katz J, Yue S, Xue W. Increased risk for COVID-19 in patients with vitamin D deficiency. Nutrition 2021;84:111106.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Lips P, Cashman KD, Lamberg-Allardt C, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Bianchi ML, et al. Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: a position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society. Eur J Endocrinol 2019;180:P23-P54.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Abdollahi A, Kamali Sarvestani H, Rafat Z, Ghaderkhani S, Mahmoudi-Aliabadi M, Jafarzadeh B, et al. The association between the level of serum 25(OH) vitamin D, obesity, and underlying diseases with the risk of developing COVID-19 infection: a case-control study of hospitalized patients in Tehran, Iran. J Med Virol 2021;93:2359-2364.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Baktash V, Hosack T, Patel N, Shah S, Kandiah P, Van den Abbeele K, et al. Vitamin D status and outcomes for hospitalised older patients with COVID-19. Postgrad Med J 2021;97:442-447.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Campi I, Gennari L, Merlotti D, Mingiano C, Frosali A, Giovanelli L, et al. Vitamin D and COVID-19 severity and related mortality: a prospective study in Italy. BMC Infect Dis 2021;21:566.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Cereda E, Bogliolo L, Klersy C, Lobascio F, Masi S, Crotti S, et al. Vitamin D 25OH deficiency in COVID-19 patients admitted to a tertiary referral hospital. Clin Nutr 2021;40:2469-2472.ArticlePubMed
- 31. De Smet D, De Smet K, Herroelen P, Gryspeerdt S, Martens GA. Vitamin D deficiency as risk factor for severe COVID-19: a convergence of two pandemics. MedRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 [cited 2020 Dec 25]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.01.20079376.Article
- 32. Hernández JL, Nan D, Fernandez-Ayala M, García-Unzueta M, Hernández-Hernández MA, López-Hoyos M, et al. Vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2021;106:e1343-e1353.Article
- 33. Israel A, Cicurel AA, Feldhamer I, Dror Y, Giveon SM, Gillis D, et al. The link between vitamin D deficiency and Covid-19 in a large population. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 [cited 2020 Dec 28]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.04.20188268.Article
- 34. Karahan S, Katkat F. Impact of serum 25(OH) vitamin D level on mortality in patients with COVID-19 in Turkey. J Nutr Health Aging 2021;25:189-196.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Li S, Cao Z, Yang H, Zhang Y, Xu F, Wang Y. Metabolic healthy obesity, vitamin D status, and risk of COVID-19. Aging Dis 2021;12:61-71.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Livingston M, Plant A, Dunmore S, Hartland A, Jones S, Laing I, et al. Detectable respiratory SARS-CoV-2 RNA is associated with low vitamin D levels and high social deprivation. Int J Clin Pract 2021;75:e14166.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Luo X, Liao Q, Shen Y, Li H, Cheng L. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with COVID-19 incidence and disease severity in Chinese people. J Nutr 2021;151:98-103.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Macaya F, Espejo Paeres C, Valls A, Fernández-Ortiz A, González Del Castillo J, Martín-Sánchez FJ, et al. Interaction between age and vitamin D deficiency in severe COVID-19 infection. Nutr Hosp 2020;37:1039-1042.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Maghbooli Z, Ebrahimi M, Shirvani A, Nasiri M, Pazoki M, Kafan S, et al. Vitamin D sufficiency reduced risk for morbidity and mortality in COVID-19 patients. SSRN [Preprint]. 2020 [cited 2020 Dec 28]. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3616008.Article
- 40. Mardani R, Alamdary A, Mousavi Nasab SD, Gholami R, Ahmadi N, Gholami A. Association of vitamin D with the modulation of the disease severity in COVID-19. Virus Res 2020;289:198148.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Meltzer DO, Best TJ, Zhang H, Vokes T, Arora V, Solway J. Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results. JAMA Netw Open 2020;3:e2019722.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Mendy A, Apewokin S, Wells AA, Morrow AL. Factors associated with hospitalization and disease severity in a racially and ethnically diverse population of COVID-19 patients. MedRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 [cited 2020 Dec 29]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.25.20137323.Article
- 43. Merzon E, Tworowski D, Gorohovski A, Vinker S, Golan Cohen A, Green I, et al. Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study. FEBS J 2020;287:3693-3702.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Panagiotou G, Tee SA, Ihsan Y, Athar W, Marchitelli G, Kelly D, et al. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 are associated with greater disease severity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2020;93:508-511.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 45. Radujkovic A, Hippchen T, Tiwari-Heckler S, Dreher S, Boxberger M, Merle U. Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients. Nutrients 2020;12:2757.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 46. Vassiliou AG, Jahaj E, Pratikaki M, Keskinidou C, Detsika M, Grigoriou E, et al. Vitamin D deficiency correlates with a reduced number of natural killer cells in intensive care unit (ICU) and non-ICU patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Hellenic J Cardiol 2021;62:381. 383.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Ye K, Tang F, Liao X, Shaw BA, Deng M, Huang G, et al. Does serum vitamin D level affect COVID-19 infection and its severity?- A case-control study. J Am Coll Nutr 2020;Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2020.1826005.Article
- 48. Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. [cited 2021 Jan 10]. Available from: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
- 49. Wise J. Covid-19: new coronavirus variant is identified in UK. BMJ 2020;371:m4857.ArticlePubMed
- 50. Bleizgys A. Vitamin D and COVID-19: it is time to act. Int J Clin Pract 2021;75:e13748.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Grant WB, Giovannucci E. The possible roles of solar ultravioletB radiation and vitamin D in reducing case-fatality rates from the 1918-1919 influenza pandemic in the United States. Dermatoendocrinol 2009;1:215-219.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 52. Hastie CE, Mackay DF, Ho F, Celis-Morales CA, Katikireddi SV, Niedzwiedz CL, et al. Corrigendum to “Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank”. Diabetes Metabol Syndr Clin Res Rev 2020;14:1315-1316.Article
- 53. Hastie CE, Mackay DF, Ho F, Celis-Morales CA, Katikireddi SV, Niedzwiedz CL, et al. Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank. Diabetes Metab Syndr 2020;14:561-565.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 54. Pamukçu E, Kaya MO. Letter to editor “vitamin D deficiency aggravates covid-19: systematic review and meta-analysis”. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2021;Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1951650.Article
- 55. Martineau AR, Jolliffe DA, Hooper RL, Greenberg L, Aloia JF, Bergman P, et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ 2017;356:i6583.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 56. Bilezikian JP, Bikle D, Hewison M, Lazaretti-Castro M, Formenti AM, Gupta A, et al. Mechanisms in endocrinology: vitamin D and COVID-19. Eur J Endocrinol 2020;183:R133--R147.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 57. Greiller CL, Martineau AR. Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D. Nutrients 2015;7:4240-4270.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 58. Zhou YF, Luo BA, Qin LL. The association between vitamin D deficiency and community-acquired pneumonia: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e17252.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 59. Tsujino I, Ushikoshi-Nakayama R, Yamazaki T, Matsumoto N, Saito I. Pulmonary activation of vitamin D3 and preventive effect against interstitial pneumonia. J Clin Biochem Nutr 2019;65:245-251.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 60. Thickett DR, Moromizato T, Litonjua AA, Amrein K, Quraishi SA, Lee-Sarwar KA, et al. Association between prehospital vitamin D status and incident acute respiratory failure in critically ill patients: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open Respir Res 2015;2:e000074.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 61. Dancer RC, Parekh D, Lax S, D’Souza V, Zheng S, Bassford CR, et al. Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Thorax 2015;70:617-624.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Xu J, Yang J, Chen J, Luo Q, Zhang Q, Zhang H. Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system. Mol Med Rep 2017;16:7432-7438.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 63. Huang F, Zhang C, Liu Q, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Qin Y, et al. Identification of amitriptyline HCl, flavin adenine dinucleotide, azacitidine and calcitriol as repurposing drugs for influenza A H5N1 virus-induced lung injury. PLoS Pathog 2020;16:e1008341.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 64. Rhodes JM, Subramanian S, Laird E, Kenny RA. Editorial: low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2020;51:1434-1437.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 65. Shaman J, Pitzer VE, Viboud C, Grenfell BT, Lipsitch M. Absolute humidity and the seasonal onset of influenza in the continental United States. PLoS Biol 2010;8:e1000316.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 66. Caricchio R, Gallucci M, Dass C, Zhang X, Gallucci S, Fleece D, et al. Preliminary predictive criteria for COVID-19 cytokine storm. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:88-95.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations do not affect the humoral or cellular immune response following SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations
A.H.A. Lavell, A.E. Schramade, J.J. Sikkens, K. van der Straten, K.A. van Dort, M.A. Slim, B. Appelman, L.A. van Vught, A.P.J. Vlaar, N.A. Kootstra, M.J. van Gils, Y.M. Smulders, R.T. de Jongh, M.K. Bomers, Brent Appelman, Diederik Beek van de, Marije K.
Vaccine.2024; 42(7): 1478. CrossRef - The Protective Effect of Serum Levels of Vitamins C, D, and E and IgG and IgM Antibodies in Individuals Vaccinated Against COVID-19 and Experienced Disease Relapse
Ashkan Alamdary, Alireaza Gholami, Maryam Shahali, Delaram Doroud, Rasul Moukhah, Mohammad Javad Hossein Tehrani, Rajab Mardani, Nayebali Ahmadi
Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring demographical, clinical, and dietary determinants of vitamin D deficiency among adults in Douala, Cameroon during the COVID-19 era
Arlette Flore Moguem Soubgui, Wilfried Steve Ndeme Mboussi, Loick Pradel Kojom Foko, Elisée Libert Embolo Enyegue, Martin Luther Koanga Mogtomo
Heliyon.2024; 10(3): e24926. CrossRef - Dynamic Shifts in Vitamin D Status Following Liposuction: Implications for Patient Monitoring and Health
Hüseyin KANDULU
Ağrı Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2024; 2(1): 1. CrossRef - The role of vitamin D in outcomes of critical care in COVID-19 patients: evidence from an umbrella meta-analysis of interventional and observational studies
Abdolreza Jamilian, Faezeh Ghalichi, Fatemeh Hamedi Kalajahi, Nima Radkhah, Neda Jourabchi, Vali Musazadeh, Ehsan Amini-Salehi, Meysam Zarezadeh, Alireza Ostadrahimi
Public Health Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D and vitamin D binding protein levels in COVID-19 intensive care unit patients: A prospective multicenter study
Vesile Diker, Gülseren Yılmaz, Muhammed Düz, Mürvet Algemi, Mehmet Köseoğlu, Hümeyra Emre, Osman Oğuz
Journal of Medical Biochemistry.2024; 43(4): 610. CrossRef - Calcifediol boosts efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine by upregulating genes promoting memory T cell responses
Himanshu Singh Saroha, Swati Bhat, Liza Das, Pinaki Dutta, Michael F. Holick, Naresh Sachdeva, Raman Kumar Marwaha
npj Vaccines.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D Metabolism Parameters and Cytokine Profile in COVID-19 Patients with Bolus Cholecalciferol Supplementation
Tatiana L. Karonova, Arina A. Mikhaylova, Ksenia A. Golovatyuk, Alena T. Chernikova, Zoia R. Korobova, Natalia E. Liubimova, Anna A. Starshinova, Dmitry A. Kudlay, Areg A. Totolian, Evgeny V. Shlyakhto
Diagnostics.2024; 14(13): 1408. CrossRef - The role of serum vitamin D concentrations in predicting COVID-19 course and outcome
Dunja Božić, Đorđe Stevanović, Mina Poskurica, Marina Petrović
Acta Facultatis Medicae Naissensis.2024; 41(2): 244. CrossRef - Early Metabolomic and Immunologic Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators for COVID-19
Zigui Chen, Erik Fung, Chun-Kwok Wong, Lowell Ling, Grace Lui, Christopher K. C. Lai, Rita W. Y. Ng, Ryan K. H. Sze, Wendy C. S. Ho, David S. C. Hui, Paul K. S. Chan
Metabolites.2024; 14(7): 380. CrossRef - Vitamin D in the prevention or treatment of COVID-19
Adrian R. Martineau
Proceedings of the Nutrition Society.2023; 82(2): 200. CrossRef - 100 years of vitamin D. The impact of vitamin D level in the time of COVID-19 pandemic
K. A. Golovatyuk, A. A. Mikhailova, D. I. Lagutina, A. T. Chernikova, T. L. Karonova
Russian Journal for Personalized Medicine.2023; 2(6): 33. CrossRef - Vitamin D3 and COVID-19 Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Fausto Petrelli, Simone Oldani, Karen Borgonovo, Mary Cabiddu, Giuseppina Dognini, Mara Ghilardi, Maria Chiara Parati, Daniela Petro’, Lorenzo Dottorini, Carmen Rea, Veronica Lonati, Andrea Luciani, Antonio Ghidini
Antioxidants.2023; 12(2): 247. CrossRef - Genetic Variations of the Vitamin D Metabolic Pathway and COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity: Current Understanding and Existing Evidence
Nipith Charoenngam, Aunchalee Jaroenlapnopparat, Sofia K. Mettler, Ashna Grover
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 400. CrossRef - MC-Au/MSS-Z8 porous network assisted advanced electrochemical immunosensing of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3
Amandeep Kaur, Lavisha, Ganga Ram Chaudhary, Nirmal Prabhakar
Talanta.2023; 257: 124376. CrossRef - Nutritional deficiencies that may predispose to long COVID
John V. Schloss
Inflammopharmacology.2023; 31(2): 573. CrossRef - Changes in Food Consumption Trends among American Adults since the COVID-19 Pandemic
Lillie Monroe-Lord, Elgloria Harrison, Azam Ardakani, Xuejling Duan, Lily Spechler, Tia D. Jeffery, Phronie Jackson
Nutrients.2023; 15(7): 1769. CrossRef - The Role of Diet and Specific Nutrients during the COVID-19 Pandemic: What Have We Learned over the Last Three Years?
Petra Rust, Cem Ekmekcioglu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(7): 5400. CrossRef - The role of serum vitamin 25(OH)D concentration in the Covid-19 pandemic in children
Chrysoula Kosmeri, Foteini Balomenou, Dimitrios Rallis, Maria Baltogianni, Vasileios Giapros
British Journal of Nutrition.2023; 130(3): 417. CrossRef - Vitamin D metabolism parameters in hospitalized COVID-19 patients
A. A. Mikhailova, K. A. Golovatyuk, D. I. Lagutina, A. T. Chernikova, E. Yu. Vasilieva, E. S. Bykova, T. L. Karonova
Translational Medicine.2023; 10(2): 69. CrossRef - Characteristics, comorbidities and laboratory measures associated with disease severity and poor prognosis in young and elderly patients with COVID-19 admitted to medical wards in Emilia-Romagna region, Italy: a multicentre retrospective study
Sirio Fiorino, Andrea Carusi, Alessandro Zappi, Fabio Tateo, Luca Peruzzo, Melissa Zanardi, Francesco Savelli, Giulia Di Marzio, Silvia Cesaretti, Francesca Dazzani, Raffaella Francesconi , Paolo Leandri , Gianfranco Tortorici , Susanna Vicari , Dora Melu
Italian Journal of Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Six years’ experience and trends of serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D concentration and the effect of vitamin D3 consumption on these trends
László Horváth, Sara Mirani, Michael Magdy Fahmy Girgis, Szilvia Rácz, Ildikó Bácskay, Harjit Pal Bhattoa, Béla E. Tóth
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Neuroimmunological Effect of Vitamin D on Neuropsychiatric Long COVID Syndrome: A Review
Ting-Bin Chen, Ching-Mao Chang, Cheng-Chia Yang, I-Ju Tsai, Cheng-Yu Wei, Hao-Wen Yang, Chun-Pai Yang
Nutrients.2023; 15(17): 3802. CrossRef - The effect of vitamin D deficiency on the cellular immunity of patients in the early stage of COVID-19 disease
Ali Sadeg, Abbas Arrak
Bionatura.2023; 8(CSS 3): 1. CrossRef - Distribution of Vitamin D Status in a Group from Syrian Society
Talleh Almelli
Jordan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2023; 16(4): 680. CrossRef - Effects of environmental parameters and their interactions on the spreading of SARS-CoV-2 in North Italy under different social restrictions. A new approach based on multivariate analysis
Fabio Tateo, Sirio Fiorino, Luca Peruzzo, Maddalena Zippi, Dario De Biase, Federico Lari, Dora Melucci
Environmental Research.2022; 210: 112921. CrossRef - The Relation between Vitamin D Level and Lung Clearance Index in Cystic Fibrosis—A Pilot Study
Mihaela Dediu, Ioana Mihaiela Ciuca, Liviu Laurentiu Pop, Daniela Iacob
Children.2022; 9(3): 329. CrossRef - Effect of Cholecalciferol Supplementation on the Clinical Features and Inflammatory Markers in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Open-Label, Single-Center Study
Tatiana L. Karonova, Ksenia A. Golovatyuk, Igor V. Kudryavtsev, Alena T. Chernikova, Arina A. Mikhaylova, Arthur D. Aquino, Daria I. Lagutina, Ekaterina K. Zaikova, Olga V. Kalinina, Alexey S. Golovkin, William B. Grant, Evgeny V. Shlyakhto
Nutrients.2022; 14(13): 2602. CrossRef - Vitamin D Endocrine System and COVID-19: Treatment with Calcifediol
Jose Manuel Quesada-Gomez, José Lopez-Miranda, Marta Entrenas-Castillo, Antonio Casado-Díaz, Xavier Nogues y Solans, José Luis Mansur, Roger Bouillon
Nutrients.2022; 14(13): 2716. CrossRef - Impaired Vitamin D Metabolism in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients
Alexandra Povaliaeva, Viktor Bogdanov, Ekaterina Pigarova, Larisa Dzeranova, Nino Katamadze, Natalya Malysheva, Vitaliy Ioutsi, Larisa Nikankina, Liudmila Rozhinskaya, Natalia Mokrysheva
Pharmaceuticals.2022; 15(8): 906. CrossRef - Vitamin D and COVID-19. Two years of research
Andrey P. Fisenko, Svetlana G. Makarova, Dmitry S. Yasakov, Irina Yu. Pronina, Oksana A. Ereshko, Irina G. Gordeeva, Albina A. Galimova, Tamara R. Chumbadze, Evgeny Е. Emelyashenkov, Ayina M. Lebedeva
Russian Pediatric Journal.2022; 25(3): 199. CrossRef - Vitamin D as the essential immunonutrient – the evidence base update: A review
Svetlana G. Makarova, Evgeny E. Emelyashenkov, Dmitry S. Yasakov, Irina Yu. Pronina, Oksana A. Ereshko, Irina G. Gordeeva, Albina A. Galimova, Tamara R. Chumbadze, Ayina M. Lebedeva
Pediatrics. Consilium Medicum.2022; (2): 133. CrossRef - COVID-19 Severity and Mortality in Two Pandemic Waves in Poland and Predictors of Poor Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Hospitalized Young Adults
Laura Ziuzia-Januszewska, Marcin Januszewski, Joanna Sosnowska-Nowak, Mariusz Janiszewski, Paweł Dobrzyński, Alicja A. Jakimiuk, Artur J. Jakimiuk
Viruses.2022; 14(8): 1700. CrossRef - Serum vitamin D levels and COVID-19 during pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Sadegh Mazaheri-Tehrani, Mohammad Hossein Mirzapour, Maryam Yazdi, Mohammad Fakhrolmobasheri, Amir Parsa Abhari
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2022; 51: 120. CrossRef - Administration of vitamin D and its metabolites in critically ill adult patients: an updated systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Johannes Menger, Zheng-Yii Lee, Quirin Notz, Julia Wallqvist, M. Shahnaz Hasan, Gunnar Elke, Martin Dworschak, Patrick Meybohm, Daren K. Heyland, Christian Stoppe
Critical Care.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevention of covid-19 and other acute respiratory infections with cod liver oil supplementation, a low dose vitamin D supplement: quadruple blinded, randomised placebo controlled trial
Sonja H Brunvoll, Anders B Nygaard, Merete Ellingjord-Dale, Petter Holland, Mette Stausland Istre, Karl Trygve Kalleberg, Camilla L Søraas, Kirsten B Holven, Stine M Ulven, Anette Hjartåker, Trond Haider, Fridtjof Lund-Johansen, John Arne Dahl, Haakon E M
BMJ.2022; : e071245. CrossRef - Adipokines, and not vitamin D, associate with antibody immune responses following dual BNT162b2 vaccination within individuals younger than 60 years
Mariana Pavel-Tanasa, Daniela Constantinescu, Corina Maria Cianga, Ecaterina Anisie, Ana Irina Mereuta, Cristina Gabriela Tuchilus, Petru Cianga
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D intoxication induced severe hypercalcemia from self-medication for COVID-19 infection: a public health problem?
Stefano PINI, Giuseppe SCAPARROTTA, Valentina DI VICO, Antonio FRAGASSO, Lucia F. STEFANELLI, Federico NALESSO, Lorenzo A. CALÒ
Minerva Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel CYP11A1-Derived Vitamin D and Lumisterol Biometabolites for the Management of COVID-19
Shariq Qayyum, Radomir M. Slominski, Chander Raman, Andrzej T. Slominski
Nutrients.2022; 14(22): 4779. CrossRef - COVID-19 Prevention: Vitamin D Is Still a Valid Remedy
Rachel Nicoll, Michael Y. Henein
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(22): 6818. CrossRef - Integrated bioinformatics and in silico approaches reveal the biological targets and molecular mechanisms of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D against COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus
Fanqiang Zeng, Yongli Xu, Chaoling Tang, Zhigang Yan, Chaohe Wei
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Can vitamin D status influence seroconversion to SARS-COV2 vaccines?
Endrit Shahini, Francesco Pesce, Antonella Argentiero, Antonio Giovanni Solimando
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Cholecalciferol as part of complex therapy for acute COVID-19
K.A. Golovatyuk, T.L. Karonova, A.A. Mikhailova, D.I. Lagutina, A.T. Chernikova, E.Yu. Vasilieva, E.V. Shlyakhto
Profilakticheskaya meditsina.2022; 25(12): 106. CrossRef - Vitamin D Metabolism Gene Polymorphisms and Their Associated Disorders: A
Literature Review
Mohamed Abouzid, Franciszek Główka, Leonid Kagan, Marta Karaźniewicz-Łada
Current Drug Metabolism.2022; 23(8): 630. CrossRef - Nutraceuticals in prevention and management of COVID-19
Ivana Đuričić, Milica Zrnić-Ćirić, Bojana Vidović, Vanja Todorović, Nevena Dabetić, Nevena Ivanović
Hrana i ishrana.2021; 62(2): 7. CrossRef
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Dietary intake and cancer incidence in Korean adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- Associations of daily diet-related greenhouse gas emissions with the incidence and mortality of chronic diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies
- The prevalence of Q fever in the Eastern Mediterranean region: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- The relationship between metabolic syndrome and its components with bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies

 KSE
KSE
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite