Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Epidemiol Health > Volume 42; 2020 > Article
-
COVID-19
Special Article
Epidemiologic characteristics of early cases with 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) disease in Korea -
Moran Ki1
 , Task Force for 2019-nCoV
, Task Force for 2019-nCoV -
Epidemiol Health 2020;42:e2020007.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4178/epih.e2020007
Published online: February 9, 2020
1Department of Cancer Control and Population Health, Graduate School of Cancer Science and Policy, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea
- Correspondence: Moran Ki Department of Cancer Control and Policy, Graduate School of Cancer Science and Policy, National Cancer Center, 323 Ilsan-ro, Ilsandong-gu, Goyang 410-769, Korea E-mail: moranki@naver.com
- *A full list of the members of Task Force for 2019-nCoVTeam is provided in the acknowledgments.
©2020, Korean Society of Epidemiology
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
- In about 20 days since the diagnosis of the first case of the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Korea on January 20, 2020, 28 cases have been confirmed. Fifteen patients (53.6%) of them were male and median age of was 42 years (range, 20-73). Of the confirmed cases, 16, 9, and 3 were index (57.2%), first-generation (32.1%), and second-generation (10.7%) cases, respectively. All first-generation and second-generation patients were family members or intimate acquaintances of the index cases with close contacts. Fifteen among 16 index patients had entered Korea from January 19 to 24, 2020 while 1 patient had entered Korea on January 31, 2020. The average incubation period was 3.9 days (median, 3.0), and the reproduction number was estimated as 0.48. Three of the confirmed patients were asymptomatic when they were diagnosed. Epidemiological indicators will be revised with the availability of additional data in the future. Sharing epidemiological information among researchers worldwide is essential for efficient preparation and response in tackling this new infectious disease.
- On the last day of 2019, Chinese authorities officially announced that they were managing an outbreak of pneumonia with an unknown cause. The date of onset for the initial case of this new infectious disease remains unclear. According to a report published by the medical team in Wuhan, China, on the 41 cases of this infection that occurred between December 1, 2019 and January 2, 2020, the initial patient reportedly experienced symptom-onset on December 1, 2019, although he reportedly had never visited the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market [1]. Therefore, it is likely that there was an unknown index patient, if this patient was infected by another person.
- On January 7, 2020, the idiopathic pneumonia was reported to have been caused by a new coronavirus, and information regarding the organism was made available to researchers around the world [2]. The World Health Organization (WHO) tentatively named this new virus as the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). On January 10, 2020, the first death caused by this new infectious disease was reported in China. On January 13, the first confirmed case outside China was reported in Thailand, and the patient did not have a history of visiting the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market. Thereafter, first cases were reported in Japan and Korea on January 15, 2020 and January 20, 2020, respectively. Since then, as of February 8, 2020, total number of confirmed cases in Korea have increased to 24 [3]. As epidemiologic characteristics of this new disease are unknown, they are being investigated based on comparisons with the clinically similar Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome and the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome. Rapid investigation and determination of epidemiologic characteristics of new infectious diseases is crucial for limiting transmission and for attaining desirable treatment outcomes through early diagnosis and management. Sharing of crucial data, as unearthed by epidemiologists around the world, is highly critical and it could help to definitively determine characteristics of this new infectious disease and containing its additional spread accordingly is urgent.
- This is a report reviewing the epidemiologic characteristics based on data of 28 patients in Korea between January 20, 2020 and February 10, 2020. The information may be revised on the basis of updated epidemiologic information.
INTRODUCTION
- This report was compiled using information from the epidemiologic investigation report by Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC), and from additional data confirmed and announced by the press [3,4]. As dates of the onset of symptom were recorded based on patients’ statements, initial, mild symptoms might have been overlooked. Incubation period refers to the time-interval from the time of infection to the time of onset of symptoms. However, there are many cases in which exact time of infection is not clear. When multiple instances of contact with other patients were reported, maximum and minimum incubation periods have been determined, based on the time-interval between the initial and the final time point of contact. This epidemic in Korea are composed of several index patients who were infected in foreign countries such as China, first-generation patients who were estimated to be infected by index cases, and second-generation patients who were estimated to be infected by first-generation patients. Index case means initially detected patient in the first outbreak cluster. The first patient responsible for the outbreak may not be an index case. The source of infection to which index patients in Korea were exposed needs to be identified in further investigation and this study does not include it.
- The generation time or serial interval means the time-interval between the date of symptom-onset of an index case and the date of symptom-onset of the subsequently infected patient.
- The terms of “quarantine” and “isolation” needs to be carefully distinguished. In this report, the term “quarantine” is used to indicate that cases were selected as control target and segregated by the quarantine authority as contacted persons, considering their history of contact with another confirmed patient and/or their visit to the area of the outbreak (Wuhan city or the Hubei province). “Isolation” is used when the cases were confirmed to have been infected and segregated in a medical institute as patients.
- Ethics statement
- The ethical approval or individual consent was not applicable. Data published by the KCDC were used in this study, and therefore consents from individual patients have not been obtained.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- Epidemiologic characteristics
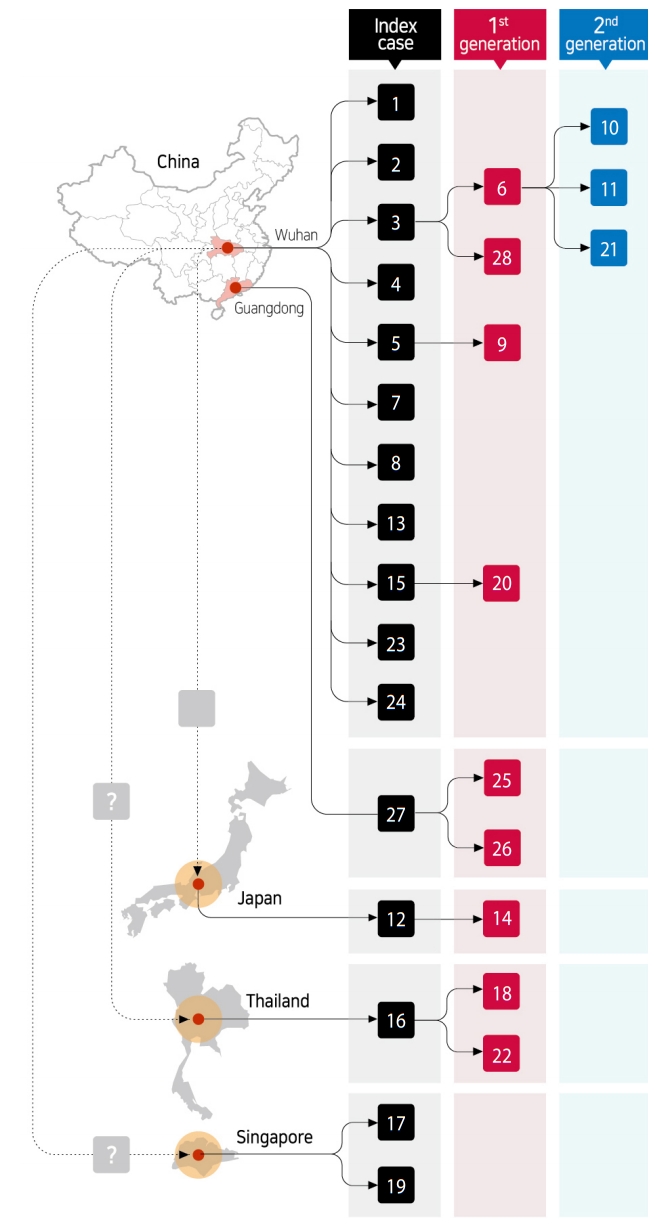
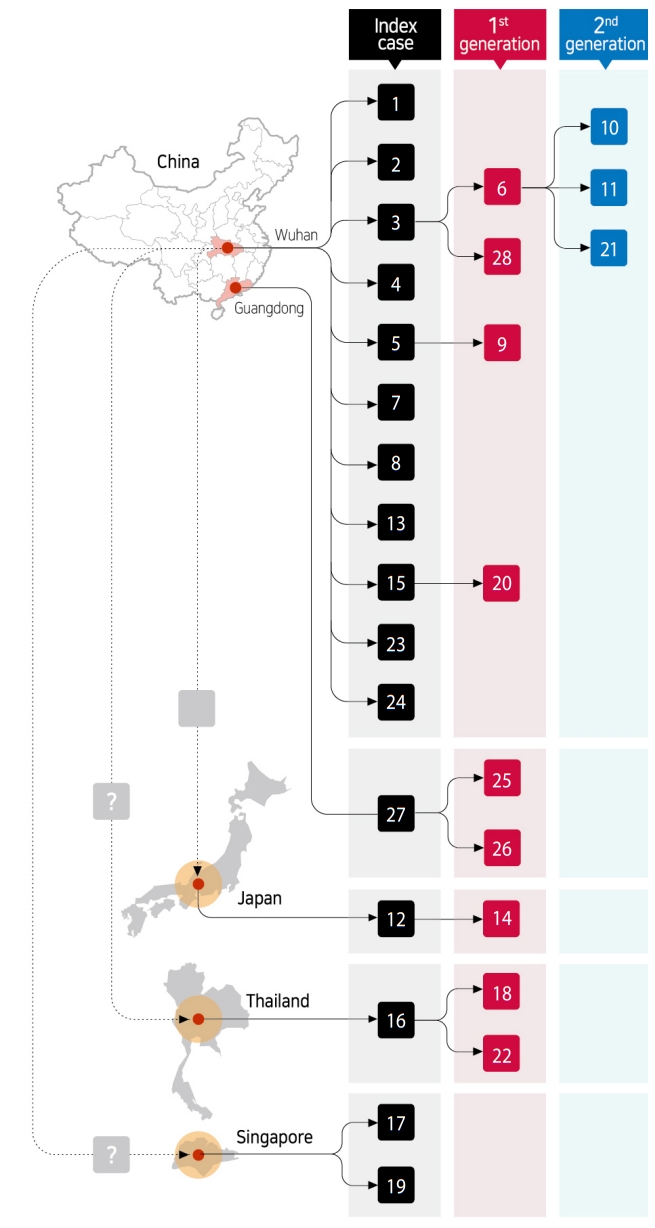
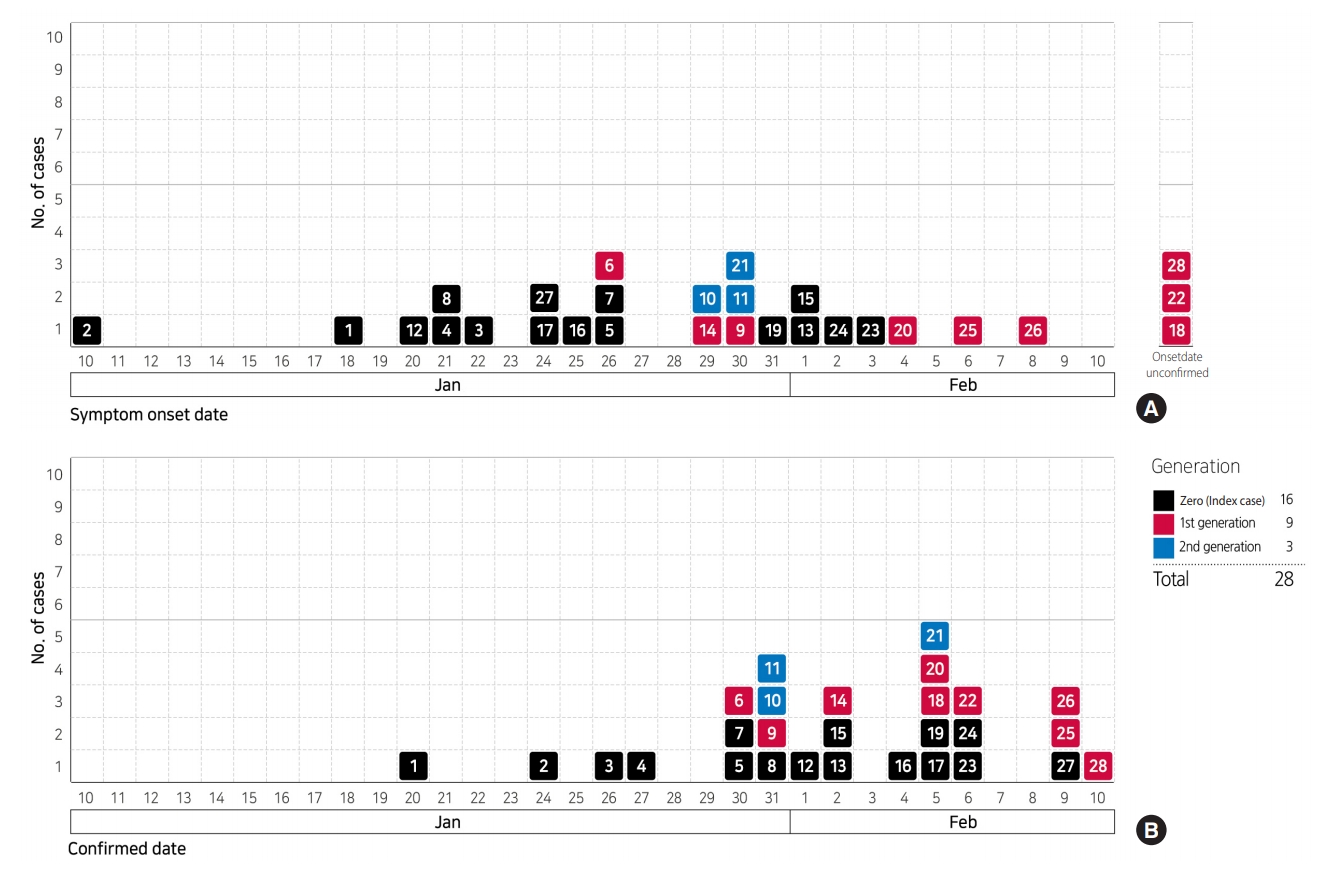
- Examination of demographic characteristics of the 28 confirmed patients in Korea showed that 15 (53.6%) and 13 (46.4%) were male and female, respectively. Six of the patients were Chinese nationals, with three identified as visitors from China, while the other three were residents in Korea. The remaining 22 patients (78.6%) were Korean nationals. The median age of all patients was 42 years (21-73) (all adults, with 6, 6, 6, 8, 1 and 1 patient in their 20s, 30s, 40s, 50s, 60s and 70s, respectively) (Table 1). In total, 16 patients constituted index cases, while 9 and 3 were first-generation and second-generation patients, respectively (Figure 1).
- Geographical regions in which 11 (68.8%), 1, 1, 1, and 2 index cases are speculated to have been infected include Wuhan, Guangdong, Japan, Thailand, and Singapore, respectively. Of the twelve first-generation and second-generation patients, 8 (66.7%) were family members of the index cases, while the remaining 4 patients were acquaintances who had been in close contact with index patients. All of these patients were identified during a control process for close contacts after confirmation index cases (Figure 1).
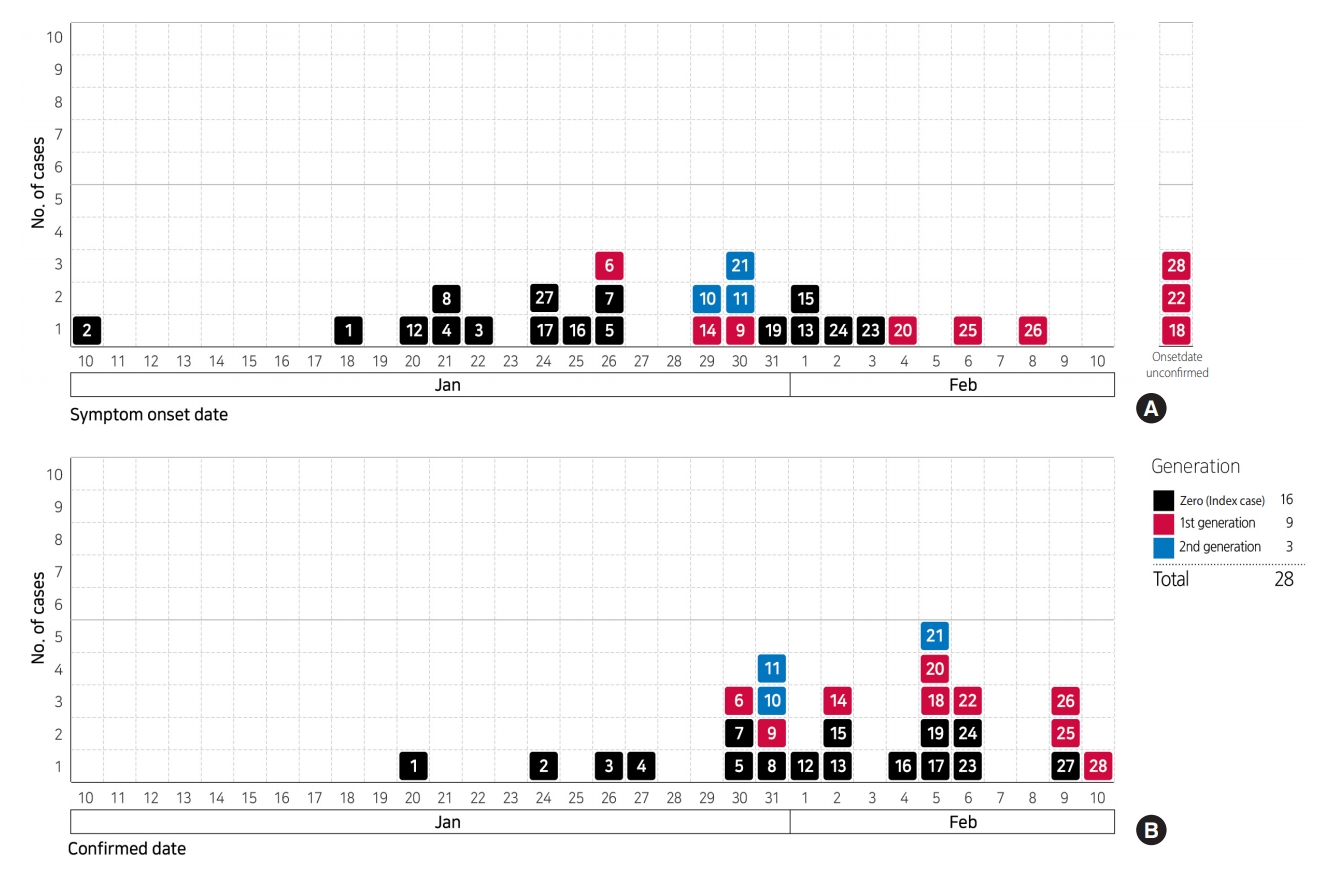
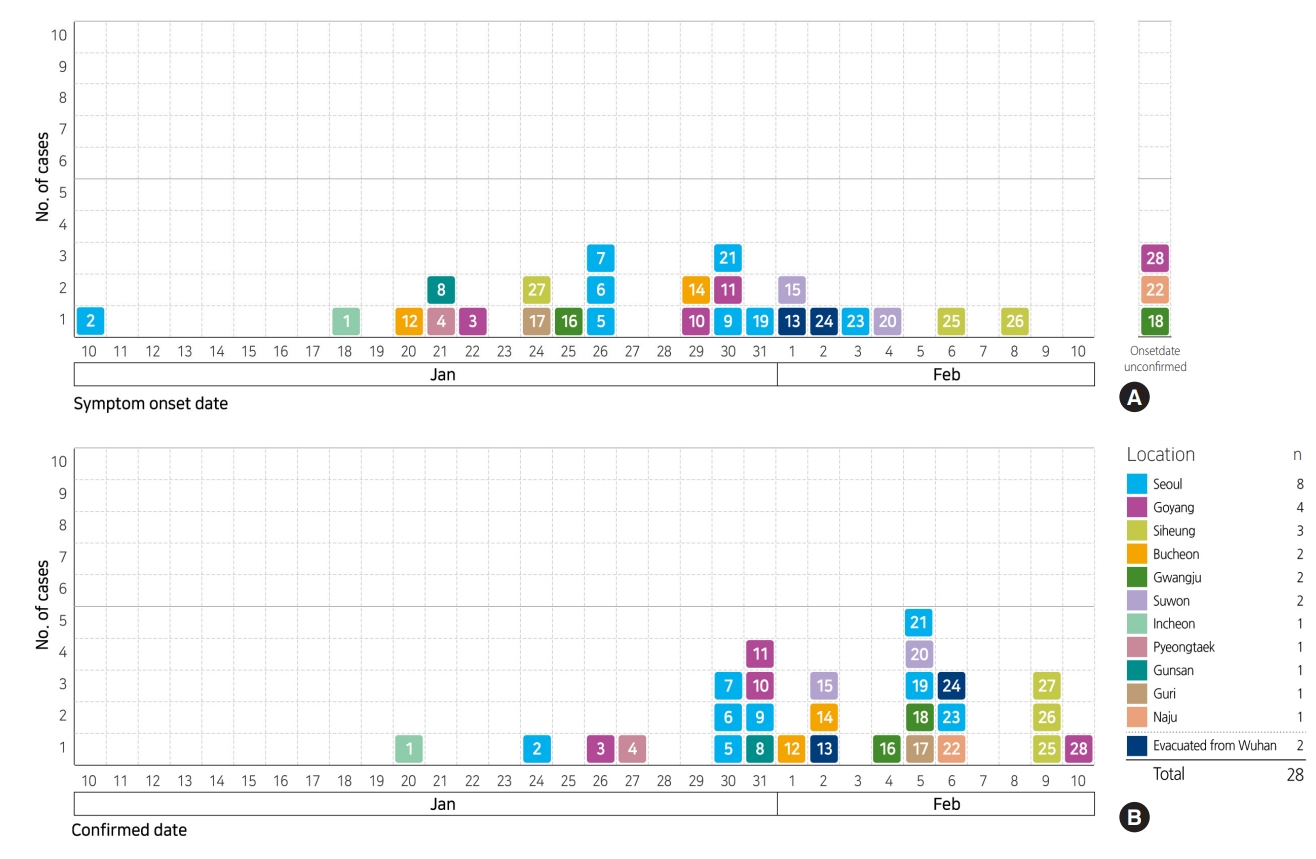
- The epidemic curve of the outbreak according to date of symptom-onset ranges from January 10, 2020 to February 8, 2020, with January 26, 2020 showing the highest number of cases (n=3). However, dates of symptom-onset show a wide distribution, overall. The epidemic curve plotted according to the date of diagnosis, ranges from January 20, 2020 to February 10, 2020 and shows that the highest number of cases were on February 5, 2020 (Figure 2). On the other hand, patient #2 first developed symptoms on January 10, 2020 while in China, and was diagnosed on January 24, 2020, after his arrival in Korea on January 22, 2020. Thus, considering only those patients who developed onset of symptoms in Korea, the initial symptom-onset of the infection occurred on January 18, 2020, in patient #1. With regard to affected geographical regions, symptom-onset occurred in Incheon, Bucheon, Pyeongtaek, Gwangju, and Goyang in order (Figure 3).
- Major areas where the diagnosed patients were exposed before being isolated, were Seoul and Gyeonggi-do with 8 and 13 cases (4, Goyang; 3, Siheung; 2, Bucheon; 1, Guri; 2, Suwon; 1, Pyeongtaek), respectively. The rest included Incheon, Gunsan, Gwangju, and Naju with 1, 1, 2, and 1 case, respectively (Figure 4). After identifying a tourist from Wuhan who visited Jeju-do (on January 21-25, 2020) and was confirmed of the infection on January 30, 2020 in China, 11 contacts of the patient were quarantined for 14 days, but were all released on February 8, 2020, after none were found to be infected.
- The time-interval for entry into Korea for the 16 index cases ranged from January 19-31, 2020, excluding that for the 2 Koreans, who were transported from Hubei in a chartered aircraft, by the Korean government, along with other Korean citizens who had been residing there (Figure 5).
- Incubation period is the time-interval between time of infection and onset of symptoms. However, as the exact time of exposure could not be ascertained in index patients and the time of symptom-onset could not be determined in those who were asymptomatic, these cases were excluded from the calculation. The estimates of incubation period included 0-15 days based on seven of the first-generation patients (#6, #20, #9, #14, #25, #26, and #28), and 1-4 days based on three of the second-generation patients (#10, #11, and #21), with mean and median values of 3.9 days (range 0-15) and 3.0 days, respectively (Table 1).
- The mean and median serial interval was estimated to be 6.6 days (range 3-15) and 4.0 days, respectively, based on data of both first-generation and second-generation patients (Table 1).
- The mean duration between symptom-onset and quarantine/isolation was 4.3 days (0-15). It was especially longer (10-12 days) in index patients who were infected in Japan, Thailand, and Singapore, which were not considered as possible risk-areas (Table 1).
- Reproduction number (R) was estimated based on data of 26 (14, index; 9, 1st generation, and 3, 2nd generation) patients among total 28 confirmed cases, excluding the 2 Korean patients who had been immediately quarantined after being transported from Wuhan and therefore did not come into contact with the Korean population. As of now, the R is estimated to be 0.48 in Korea (Poisson 95% confidence interval, 0.25 to 0.84) (Table 1).
- As of February 8, 2020, patient #6 had transmitted the infection to the highest number (n=3; 2 family members and 1 acquaintance). As super spreading event is defined when a patient transmits the infection to 5 or more people, this case has not yet been observed in Korea (Figure 5).
- Of the 28 infected patients diagnosed in Korea, 3 were asymptomatic. Of them, patients #18 and #22 were first-generation patients infected by patient #16 and these patients were asymptomatic even though they were tested positive with the virus at the beginning of quarantine.
- Of 28 patients, 4 have been discharged as of February 10, 2020. Patients #2, #1, #11, and #4 were discharged on day-13 (February 5), 19 (February 6), 11(February 10), and 15 (February 9) of hospitalization, respectively (Figure 5). There are currently no clinically serious patients among those undergoing treatment. After more patients recover and are discharged in the future, further detailed epidemiologic information (such as mean duration of hospitalization, duration of disappearance of symptoms and viral shedding since hospitalization) would be suggested.
- Patient characteristics
- Data on clinical progression, exposed contacts, and transmission of infection for each confirmed case are presented as Appendix 1.
- Baseline characteristics are shown in Figure 5.
RESULTS
- Analysis of data on confirmed cases in Korea, has yielded an incubation period of 3.9 days and median patient age of 42-year, which are lower than the incubation period of 5.2 days and the median age of 59 years announced in China [5]. The older age of patients might have increased fatality rate in China. The novel Coronavirus outbreak which originated in China at the end of 2019, is now spreading around the world. Totally, 28 cases have been confirmed in Korea as of February 10, 2020. Of these, 12 were infected in China, while 4 contracted the infection in other countries. The remaining 12 patients were infected by these index cases and were diagnosed while being monitored by the quarantine authority as contacts of confirmed patients. Therefore, community transmission with an unknown infection-cycle has not yet been occurred in Korea. Furthermore, due to blockade of the Hubei province (enforced on January 23, 2020) and limitation of group tour imposed by the Chinese government (on January 27, 2020), there have been no confirmed cases among the people travelling to Korea from China, since January 24, 2020. However, early diagnosis of patient is urgent as index cases are entering Korea from countries other than China. Fortunately, the technique of molecular diagnosis of the virus using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction, was quickly developed in Korea and has been available in medical institutions including private institutes across the country since February 7, 2020. This will allow early identification of undetected patients, thus improving their prognosis as well as preventing community transmission. WHO announced a Public Health Emergency of International Concern worldwide on January 30, 2020 [6], with an aim to cope more effectively with infectious disease, through international collaboration. It is necessary for all the countries including China, to promptly share epidemiological information on this new disease. Our epidemiology research team will keep accumulating new data and updating related indices.
DISCUSSION
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare for this study.
-
FUNDING
This research was supported by a Government-wide R&D Fund project for infectious disease research (GFID), Republic of Korea (grant No. HG18C0088).
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All work was done by MK and Task Force for 2019-nCoV.
NOTES
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS



| Characteristics | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Male | 15 (53.6) |
| Age (yr) | |
| 20-29 | 6 (21.4) |
| 30-39 | 6 (21.4) |
| 40-49 | 6 (21.4) |
| 50-59 | 8 (28.6) |
| 60-69 | 1 (3.6) |
| 70-79 | 1 (3.6) |
| Nationality | |
| Korean living in Korea | 22 (78.6) |
| Chinese living in Korea | 3 (10.7) |
| Chinese travelers from Wuhan, China | 3 (10.7) |
| Source of infection | |
| Index case (n=16) | |
| Wuhan, China | 11 (68.8) |
| Guangdong, China | 1 (6.3) |
| Singapore | 2 (12.5) |
| Japan | 1 (6.3) |
| Thailand | 1 (6.3) |
| 1st generation (n=9) | |
| #16 | 2 (22.2) |
| #3 | 2 (22.2) |
| #5 | 2 (22.2) |
| #15 | 1 (11.1) |
| #12 | 1 (11.1) |
| #15 | 1 (11.1) |
| 2nd generation (n=3) | |
| #6 | 3 (100) |
|
|
|
| Period category (d) | Average (range)/median |
|
|
|
| Incubation period1 | 3.9 (0-15)/3.0 |
| Serial interval | 6.6 (3-15)/4.0 |
| Symptom-onset to diagnosis1 | 5.2 (0-16)/4.0 |
| Symptom-onset to quarantine or isolation1 | 4.3 (0-15)/3.0 |
| Diagnosis to discharge2 | 13.0 (7-17)/12.5 |
|
|
|
| Reproduction number | Estimate (Poisson 95% CI)/[binominal 95% CI] |
|
|
|
| Total | 0.48 (0.25, 0.84)/[0.28, 0.69] |
| 1st generation (n=9) | 0.56 (0.26, 1.07)/[0.30, 0.80] |
| 2nd generation (n=3) | 0.33 (0.07, 0.97)/[0.07, 0.70] |
- 1. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020;395:497-506.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Carlos WG, Dela Cruz CS, Cao B, Pasnick S, Jamil S. Novel Wuhan (2019-nCoV) coronavirus. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2020;201:p7-p8.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Yoo JH, Hong ST. The outbreak cases with the novel coronavirus suggest upgraded quarantine and isolation in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2020;35:e62.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Current status of COVID-19 outbreak. [cited 2020 Feb 7]. Available from: http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/tcmBoardList.do?brdId= &brdGubun=&dataGubun=&ncvContSeq=&contSeq=&board_id (Korean).
- 5. Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med 2020;doi: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2001316.Article
- 6. World Health Organization. Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee regarding the outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV); 2020 Jan 30 [cited 2020 Feb 7]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-meeting-of-the-international-health-regulations-(2005)-emergency-committee-regarding-the-outbreak-of-novel-coronavirus-(2019-ncov).
REFERENCES
Appendix
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Estimating hidden relationships in dynamical systems: Discovering drivers of infection rates of COVID-19
S. Butail, A. Bhattacharya, M. Porfiri
Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal non-pharmaceutical interventions considering limited healthcare system capacity and economic costs in the Republic of Korea
Yuna Lim, Youngsuk Ko, Victoria May P. Mendoza, Renier Mendoza, Jongmin Lee, Eunok Jung
Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena.2024; 19: 6. CrossRef - Analysis of Symptoms and Demographic Characteristics in Diagnosis of COVID-19 by Logistic Regression Model
Caner Tanış
Selçuk Üniversitesi Fen Fakültesi Fen Dergisi.2024; 50(1): 1. CrossRef - Combating the Progression of Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
Infectious Disease: Current State and Future Prospects in
Molecular Diagnostics and Drug Discovery
Arbind Kumar, Aashish Sharma, Narendra Vijay Tirpude, Sharad Thakur, Sanjay Kumar
Current Molecular Medicine.2023; 23(2): 127. CrossRef - Modeling the impact of combined use of COVID Alert SA app and vaccination to curb COVID-19 infections in South Africa
Musyoka Kinyili, Justin B. Munyakazi, Abdulaziz Y. A. Mukhtar, Jun Tanimoto
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(2): e0264863. CrossRef - Modelling the effects of social distancing, antiviral therapy, and booster shots on mitigating Omicron spread
Jongmin Lee, Renier Mendoza, Victoria May P. Mendoza, Jacob Lee, Yubin Seo, Eunok Jung
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The transmission pattern and clinical course of the first 417 patients with COVID-19 infection in Shenzhen, China
Yizi Zheng, Zhenhan Deng, Feijuan Huang, Yu Zhang, Yuanzhe Cai, Jingyue Su, Zhengzhi Wu, Shiwei Yang
Journal of International Medical Research.2023; 51(5): 030006052311743. CrossRef - Vaccine effectiveness and the epidemiological characteristics of a COVID-19 outbreak in a tertiary hospital in Republic of Korea
Seonhee Ahn, Tae Jong Son, Yoonsuk Jang, Jihyun Choi, Young Joon Park, Jiseon Seong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Muk Ju Kim, Donghyok Kwon
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(3): 188. CrossRef - Evaluation of the EsteR Toolkit for COVID-19 Decision Support: Sensitivity Analysis and Usability Study
Rieke Alpers, Lisa Kühne, Hong-Phuc Truong, Hajo Zeeb, Max Westphal, Sonja Jäckle
JMIR Formative Research.2023; 7: e44549. CrossRef - Assessing changes in incubation period, serial interval, and generation time of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiangyanyu Xu, Yanpeng Wu, Allisandra G. Kummer, Yuchen Zhao, Zexin Hu, Yan Wang, Hengcong Liu, Marco Ajelli, Hongjie Yu
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Asthma and risk of infection, hospitalization, ICU admission and mortality from COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Anthony P. Sunjaya, Sabine M. Allida, Gian Luca Di Tanna, Christine Jenkins
Journal of Asthma.2022; 59(5): 866. CrossRef - Incubation period for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Balram Rai, Anandi Shukla, Laxmi Kant Dwivedi
Journal of Public Health.2022; 30(11): 2649. CrossRef - Serial Intervals and Case Isolation Delays for Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sheikh Taslim Ali, Amy Yeung, Songwei Shan, Lin Wang, Huizhi Gao, Zhanwei Du, Xiao-Ke Xu, Peng Wu, Eric H Y Lau, Benjamin J Cowling
Clinical Infectious Diseases.2022; 74(4): 685. CrossRef - An interaction Neyman–Scott point process model for coronavirus disease-19
Jaewoo Park, Won Chang, Boseung Choi
Spatial Statistics.2022; 47: 100561. CrossRef - SARS, MERS and CoVID-19: An overview and comparison of clinical, laboratory and radiological features
Manas Pustake, Isha Tambolkar, Purushottam Giri, Charmi Gandhi
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2022; 11(1): 10. CrossRef - Forecasting COVID-19 cases by assessing control-intervention effects in Republic of Korea: A statistical modeling approach
Hyojung Lee, Geunsoo Jang, Giphil Cho
Alexandria Engineering Journal.2022; 61(11): 9203. CrossRef - Linking genomic and epidemiologic information to advance the study of COVID-19
Yiwei Wang, Jiaxin Yang, Xinhao Zhuang, Yunchao Ling, Ruifang Cao, Qingwei Xu, Peng Wang, Ping Xu, Guoqing Zhang
Scientific Data.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 outbreak and risk factors for infection in a taekwondo gym in the Republic of Korea
Seung Hwan Shin, Eonjoo Park, Sookhyun Kim, Minji Jang, Subin Park, Dong-Hwi Kim, Tae Jong Son, Ji-Hyuk Park
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2022; 13(2): 162. CrossRef - Reinfection by SARS CoV2 in Valle Del Cauca, Colombia: A Descriptive Retrospective Study
Isabel Cristina Hurtado, Juan Sebastián Hurtado, Sandra Lizeth Valencia, Elisa María Pinzón, Ana Roció Guzmán, María Cristina Lesmes
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2022; 59: 004695802210965. CrossRef - Predicting Anxiety and Depression Among Patients With COVID-19 in Concentrated Isolation at Medical Camps in Vietnam: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study
Vu Thi Thu Trang, Khoa Le Anh Huynh, Huyen Thi Truong, Hue Thi Nguyen, Giang Truong Hoang, Dat Quang Dao, Ut Van Vu, Zair Hassan, My Ngoc Ha Nguyen, Le Van Truong
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of clinical, epidemiological and paraclinical characteristics of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 and its relationship with disease severity in Amir Al-Momenin Hospital in Tehran
Masoumeh Mesgarian, Termeh Tarjoman, Masuod Karimloo, Mahnaz Valizadeh, Zahra Hanifezadeh, Omid Ameli, Mohsen Alijani, Behnam Farhoodi, Mehrangiz Zangeneh
MEDICAL SCIENCES JOURNAL.2022; 32(1): 64. CrossRef - Mathematical modeling of the impact of Omicron variant on the COVID-19 situation in South Korea
Jooha Oh, Catherine Apio, Taesung Park
Genomics & Informatics.2022; 20(2): e22. CrossRef - Do the Self-Reported Changes in Physical Activity After the Emergence of the COVID-19 Pandemic Associate With Major Depression According to Moderate to Vigorous Physical Activity Status?
Jeong Hyun Ahn, Jin Young Nam
Journal of Physical Activity and Health.2022; 19(7): 518. CrossRef - Development of Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Test for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Virus Antigens in Clinical Specimens
Rafik Hamed Sayed, Mohamed Samy Abousenna, Shaimaa Abdelall Elsaady, Rafik Soliman, Mohamed Ahmed Saad
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(14): 2477. CrossRef - Incubation period of wild type of SARS-CoV-2 infections by age, gender, and epidemic periods
Chiara Achangwa, Huikyung Park, Sukhyun Ryu
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Multiscale Model of COVID-19 Dynamics
Xueying Wang, Sunpeng Wang, Jin Wang, Libin Rong
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - An update of serial interval estimates for COVID-19: a meta-analysis
Jean-François Jusot
4open.2022; 5: 16. CrossRef - Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in the community based on participants in the 2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ah-Ra Kim, Dohsik Minn, Su Hwan Kim, Hyeon Nam Do, Byoungguk Kim, Young Sill Choi, Dong-Hyun Kim, Eun-Jee Oh, Kyungwon Oh, Donghyok Kwon, Jun-Wook Kwon, Sung Soon Kim, June-Woo Lee
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022028. CrossRef - Adjusting non-pharmaceutical interventions based on hospital bed capacity using a multi-operator differential evolution
Victoria May P. Mendoza, Renier Mendoza, Jongmin Lee, Eunok Jung
AIMS Mathematics.2022; 7(11): 19922. CrossRef - Quantifying the Effects of Non-Pharmaceutical and Pharmaceutical Interventions Against Covid-19 Epidemic in the Republic of Korea: Mathematical Model-Based Approach Considering Age Groups and the Delta Variant
Youngsuk Ko, Victoria May P. Mendoza, Yubin Seo, Jacob Lee, Yeonju Kim, Donghyok Kwon, Eunok Jung, E. Augeraud, M. Banerjee, J.-S. Dhersin, A. d'Onofrio, T. Lipniacki, S. Petrovskii, Chi Tran, A. Veber-Delattre, E. Vergu, V. Volpert
Mathematical Modelling of Natural Phenomena.2022; 17: 39. CrossRef - Modelling the Potential Impact of Stigma on the Transmission Dynamics of COVID-19 in South Africa
Siphokazi Princess Gatyeni, Faraimunashe Chirove, Farai Nyabadza
Mathematics.2022; 10(18): 3253. CrossRef - COVID‐19 in one region of New Zealand: a descriptive epidemiological study
Vanessa Hammond, Michael Butchard, Hohepa Stablein, Susan Jack
Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health.2022; 46(6): 745. CrossRef - Hospital variations during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic in a referral hospital in a low-to-middle-income country: a large single-center cohort study
Carmelo Dueñas-Castell, Wilfrido Coronell, Diana Borré-Naranjo, Amilkar Almanza, Leydis Lora Lián, Rafael Navarro, Jose Rojas-Suarez
Revista Ciencias Biomédicas.2022; 11(2): 103. CrossRef - Viral shedding patterns of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections by periods of variant predominance and vaccination status in Gyeonggi Province, Korea
Gawon Choi, Ah-Young Lim, Sojin Choi, Kunhee Park, Soon Young Lee, Jong-Hun Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 45: e2023008. CrossRef - A systematic review of asymptomatic infections with COVID-19
Zhiru Gao, Yinghui Xu, Chao Sun, Xu Wang, Ye Guo, Shi Qiu, Kewei Ma
Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection.2021; 54(1): 12. CrossRef - Estimates of serial interval for COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Balram Rai, Anandi Shukla, Laxmi Kant Dwivedi
Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health.2021; 9: 157. CrossRef - A model based on cellular automata to estimate the social isolation impact on COVID-19 spreading in Brazil
P.H.T. Schimit
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine.2021; 200: 105832. CrossRef - Spread of COVID-19 and policy responses in Vietnam: An overview
Quang Van Nguyen, Dung Anh Cao, Son Hong Nghiem
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2021; 103: 157. CrossRef - Período de incubación de la COVID-19: revisión sistemática y metaanálisis
J.A. Quesada, A. López-Pineda, V.F. Gil-Guillén, J.M. Arriero-Marín, F. Gutiérrez, C. Carratala-Munuera
Revista Clínica Española.2021; 221(2): 109. CrossRef - Clinical, epidemiological, laboratory, and radiological characteristics of novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in retrospective studies: A systemic review and meta-analysis
Ebrahim Kouhsari, Khalil Azizian, Mohammad Sholeh, Mohammad Shayestehpour, Marzieh Hashemian, Somayeh Karamollahi, Sajad Yaghoubi, Nourkhoda Sadeghiifard
Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology.2021; 39(1): 104. CrossRef - Incubation period of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
J.A. Quesada, A. López-Pineda, V.F. Gil-Guillén, J.M. Arriero-Marín, F. Gutiérrez, C. Carratala-Munuera
Revista Clínica Española (English Edition).2021; 221(2): 109. CrossRef - Comparative profile for COVID-19 cases from China and North America: Clinical symptoms, comorbidities and disease biomarkers
Alaa Badawi, Denitsa Vasileva
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(1): 118. CrossRef - Serial Interval and Generation Interval for Imported and Local Infectors, Respectively, Estimated Using Reported Contact-Tracing Data of COVID-19 in China
Menghui Li, Kai Liu, Yukun Song, Ming Wang, Jinshan Wu
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID‐19 and Immunological Dysregulation: Can Autoantibodies be Useful?
Simona Pascolini, Antonio Vannini, Gaia Deleonardi, Michele Ciordinik, Annamaria Sensoli, Ilaria Carletti, Lorenza Veronesi, Chiara Ricci, Alessia Pronesti, Laura Mazzanti, Ana Grondona, Tania Silvestri, Stefano Zanuso, Marcello Mazzolini, Claudine Lalann
Clinical and Translational Science.2021; 14(2): 502. CrossRef - Delving Into the Origin of Destructive Inflammation in COVID-19: A Betrayal of Natural Host Defense Peptides?
Rebeca Garcia-Fandino, Ángel Piñeiro
Frontiers in Immunology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Subcritical Transmission in the Early Stage of COVID-19 in Korea
Yong Sul Won, Jong-Hoon Kim, Chi Young Ahn, Hyojung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(3): 1265. CrossRef - Do Stay at Home Orders and Cloth Face Coverings Control COVID-19 in New York City? Results From a SIER Model Based on Real-world Data
Jian Li, Yuming Wang, Jing Wu, Jing-Wen Ai, Hao-Cheng Zhang, Michelle Gamber, Wei Li, Wen-Hong Zhang, Wen-Jie Sun
Open Forum Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Steps and Challenges in Creating and Managing Quarantine Capacity During a Global Emergency – Qatar’s Experience
Naseer Masoodi, Abdul-Badi Abou-Samra, Roberto Bertollini, Anas Halabi, Fatima Haidar, Nadya Al Anzi, Adeel A. Butt
Journal of Infection and Public Health.2021; 14(5): 598. CrossRef - COVID‐19: Current knowledge in clinical features, immunological responses, and vaccine development
Ramandeep Singh, Alisha Kang, Xiangqian Luo, Mangalakumari Jeyanathan, Amy Gillgrass, Sam Afkhami, Zhou Xing
The FASEB Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Systematic Assessment of South Korea’s Capabilities to Control COVID-19
Katelyn J. Yoo, Soonman Kwon, Yoonjung Choi, David M. Bishai
Health Policy.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology, clinical spectrum, viral kinetics and impact of COVID‐19 in the Asia‐Pacific region
Kin On Kwok, Ying Huang, Margaret Ting Fong Tsoi, Arthur Tang, Samuel Yeung Shan Wong, Wan In Wei, David Shu Cheong Hui
Respirology.2021; 26(4): 322. CrossRef - COVID-19: Famotidine, Histamine, Mast Cells, and Mechanisms
Robert W. Malone, Philip Tisdall, Philip Fremont-Smith, Yongfeng Liu, Xi-Ping Huang, Kris M. White, Lisa Miorin, Elena Moreno, Assaf Alon, Elise Delaforge, Christopher D. Hennecker, Guanyu Wang, Joshua Pottel, Robert V. Blair, Chad J. Roy, Nora Smith, Jul
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment and management of asymptomatic COVID-19 infection: A systematic review
Joshuan J. Barboza, Diego Chambergo-Michilot, Mariana Velasquez-Sotomayor, Christian Silva-Rengifo, Carlos Diaz-Arocutipa, Jose Caballero-Alvarado, Franko O. Garcia-Solorzano, Christoper A. Alarcon-Ruiz, Leonardo Albitres-Flores, German Malaga, Patricia S
Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease.2021; 41: 102058. CrossRef - COVID-19 Detection Empowered with Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques: A Systematic Review
Amir Rehman, Muhammad Azhar Iqbal, Huanlai Xing, Irfan Ahmed
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(8): 3414. CrossRef - Ongoing COVID-19 Pandemic: A Concise but Updated Comprehensive Review
Chao Wang, Xiong Xiao, Hongyan Feng, Zhengyuan Hong, Meng Li, Ning Tu, Xuerong Li, Ke Wang, Lihong Bu
Current Microbiology.2021; 78(5): 1718. CrossRef - Differentially expressed immune response genes in COVID-19 patients based on disease severity
Shasha Li, Xiaoqiong Duan, Yujia Li, Ming Li, Yong Gao, Tuantuan Li, Shilin Li, Lin Tan, Tuo Shao, Andre J. Jeyarajan, Limin Chen, Mingfeng Han, Wenyu Lin, Xiuyong Li
Aging.2021; 13(7): 9265. CrossRef - Assessment of basic reproductive number for COVID-19 at global level
Cheng-Jun Yu, Zi-Xiao Wang, Yue Xu, Ming-Xia Hu, Kai Chen, Gang Qin
Medicine.2021; 100(18): e25837. CrossRef - Challenges Caused by Imported Cases Abroad for the Prevention and Control of COVID-19 in China
Jianfei Zhu, Qingqing Zhang, Chenghui Jia, Shuonan Xu, Jie Lei, Jiakuan Chen, Yanmin Xia, Wenchen Wang, Xuejiao Wang, Miaomiao Wen, Hongtao Wang, Zhipei Zhang, Wuping Wang, Jinbo Zhao, Tao Jiang
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients in Northwestern China Who Had a History of Exposure in Wuhan City: Departure Time-Originated Pinpoint Surveillance
Qingqing Zhang, Jianfei Zhu, Chenghui Jia, Shuonan Xu, Tao Jiang, Shengyu Wang
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inherently high uncertainty in predicting the time evolution of epidemics
Seung-Nam Park, Hyong-Ha Kim, Kyoung Beom Lee
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021014. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccine Priority Strategy Using a Heterogenous Transmission Model Based on Maximum Likelihood Estimation in the Republic of Korea
Youngsuk Ko, Jacob Lee, Yeonju Kim, Donghyok Kwon, Eunok Jung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(12): 6469. CrossRef - Is it enough for COVID-19 screening test? Limitation of swab test and general characteristics of mild symptom patients
Sungwoo Choi, Hyo Jeong Choi, Ho Jung Kim
Science Progress.2021; 104(2): 003685042110261. CrossRef - Quality of life during the epidemic of COVID-19 and its associated factors among enterprise workers in East China
Xiaoxiao Chen, Qian Xu, Haijiang Lin, Jianfu Zhu, Yue Chen, Qi Zhao, Chaowei Fu, Na Wang
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Rapid and Visual Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using Multiplex Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Linked With Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor
Xu Chen, Qingxue Zhou, Shijun Li, Hao Yan, Bingcheng Chang, Yuexia Wang, Shilei Dong
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Non-lockdown Social Distancing and Testing-Contact Tracing During a COVID-19 Outbreak in Daegu, South Korea, February to April 2020: A Modeling Study
Yi-Hsuan Chen, Chi-Tai Fang, Yu-Ling Huang
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2021; 110: 213. CrossRef - Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Pratha Sah, Meagan C. Fitzpatrick, Charlotte F. Zimmer, Elaheh Abdollahi, Lyndon Juden-Kelly, Seyed M. Moghadas, Burton H. Singer, Alison P. Galvani
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Transmission dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in a mid-size city of China
Hongjun Zhao, Xiaoxiao Lu, Wenhui Lun, Tiegang Li, Boqi Rao, Dedong Wang, Di Wu, Fuman Qiu, Zhicong Yang, Jiachun Lu
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The incubation period of COVID-19: a global meta-analysis of 53 studies and a Chinese observation study of 11 545 patients
Cheng Cheng, DongDong Zhang, Dejian Dang, Juan Geng, Peiyu Zhu, Mingzhu Yuan, Ruonan Liang, Haiyan Yang, Yuefei Jin, Jing Xie, Shuaiyin Chen, Guangcai Duan
Infectious Diseases of Poverty.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - How Important Is Behavioral Change during the Early Stages of the COVID-19 Pandemic? A Mathematical Modeling Study
Jongmin Lee, Seok-Min Lee, Eunok Jung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(18): 9855. CrossRef - Experience from five Asia-Pacific countries during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic: Mitigation strategies and epidemiology outcomes
Clotilde El Guerche-Séblain, Lina Chakir, Gopinath Nageshwaran, Rebecca C. Harris, Caroline Sevoz-Couche, Olivier Vitoux, Philippe Vanhems
Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease.2021; 44: 102171. CrossRef - Healthcare practice strategies for integrating personalized medicine: Management of COVID-19
Wen-Yi Liu, Ching-Wen Chien, Tao-Hsin Tung
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(29): 8647. CrossRef - Rapid transmission of coronavirus disease 2019 within a religious sect in South Korea: A mathematical modeling study
Jong-Hoon Kim, Hyojung Lee, Yong Sul Won, Woo-Sik Son, Justin Im
Epidemics.2021; 37: 100519. CrossRef - Intestinal Collinsella may mitigate infection and exacerbation of COVID-19 by producing ursodeoxycholate
Masaaki Hirayama, Hiroshi Nishiwaki, Tomonari Hamaguchi, Mikako Ito, Jun Ueyama, Tetsuya Maeda, Kenichi Kashihara, Yoshio Tsuboi, Kinji Ohno, Francois Blachier
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(11): e0260451. CrossRef - Mathematical modeling and impact analysis of the use of COVID Alert SA app
Musyoka Kinyili, Justin B Munyakazi, Abdulaziz YA Mukhtar
AIMS Public Health.2021; 9(1): 106. CrossRef - One Health, “Disease X” & the challenge of “Unknown” Unknowns
Pranab Chatterjee, Parvati Nair, Matthew Chersich, Yitagele Terefe, AbhimanyuSingh Chauhan, Fabiola Quesada, Greg Simpson
Indian Journal of Medical Research.2021; 153(3): 264. CrossRef - Psychological well-being of foreign university students during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study in South Korea using the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale (K10)
Achangwa Chiara, Tae-Jun Lee, Moo-Sik Lee
Journal of Global Health Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of COVID-19 transmission in heterogeneous age groups and effective vaccination strategy in Korea: a mathematical modeling study
Youngsuk Ko, Jacob Lee, Yubin Seo, Eunok Jung
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021059. CrossRef - The SARS-CoV-2 outbreak from a one health perspective
Maged Gomaa Hemida, Mohammed M. Ba Abduallah
One Health.2020; 10: 100127. CrossRef - Clinical features of severe pediatric patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan: a single center’s observational study
Dan Sun, Hui Li, Xiao-Xia Lu, Han Xiao, Jie Ren, Fu-Rong Zhang, Zhi-Sheng Liu
World Journal of Pediatrics.2020; 16(3): 251. CrossRef - Quantifying SARS-CoV-2 transmission suggests epidemic control with digital contact tracing
Luca Ferretti, Chris Wymant, Michelle Kendall, Lele Zhao, Anel Nurtay, Lucie Abeler-Dörner, Michael Parker, David Bonsall, Christophe Fraser
Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19) in Humans: A Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis
Israel Júnior Borges do Nascimento, Nensi Cacic, Hebatullah Mohamed Abdulazeem, Thilo Caspar von Groote, Umesh Jayarajah, Ishanka Weerasekara, Meisam Abdar Esfahani, Vinicius Tassoni Civile, Ana Marusic, Ana Jeroncic, Nelson Carvas Junior, Tina Poklepovic
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(4): 941. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of COVID-19 Epidemiology Based on Current Evidence
Minah Park, Alex R. Cook, Jue Tao Lim, Yinxiaohe Sun, Borame L. Dickens
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(4): 967. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics of non-critically ill patients with novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) in a Fangcang Hospital
X. Wang, J. Fang, Y. Zhu, L. Chen, F. Ding, R. Zhou, L. Ge, F. Wang, Q. Chen, Y. Zhang, Q. Zhao
Clinical Microbiology and Infection.2020; 26(8): 1063. CrossRef - Estimating the reproductive number and the outbreak size of COVID-19 in Korea
Sunhwa Choi, Moran Ki
Epidemiology and Health.2020; 42: e2020011. CrossRef - Renal Involvement and Early Prognosis in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia
Guangchang Pei, Zhiguo Zhang, Jing Peng, Liu Liu, Chunxiu Zhang, Chong Yu, Zufu Ma, Yi Huang, Wei Liu, Ying Yao, Rui Zeng, Gang Xu
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.2020; 31(6): 1157. CrossRef - Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 136 cases of COVID-19 in main district of Chongqing
Peng Chen, Ying Zhang, Yongsheng Wen, Jinjun Guo, Jinwei Jia, Yu Ma, Yi Xu
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.2020; 119(7): 1180. CrossRef - Characteristics of asymptomatic patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection in Jinan, China
Yan Ma, Qing-nan Xu, Feng-li Wang, Xiao-man Ma, Xiao-yan Wang, Xiao-guo Zhang, Zhong-fa Zhang
Microbes and Infection.2020; 22(4-5): 212. CrossRef - An infant with a mild SARS-CoV-2 infection detected only by anal swabs: a case report
Juan Li, Jing Feng, Tian-hu Liu, Feng-cheng Xu, Guo-qiang Song
The Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases.2020; 24(3): 247. CrossRef - Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 333 confirmed cases with coronavirus disease 2019 in Shanghai, China
Xiao Yu, Xiaodong Sun, Peng Cui, Hao Pan, Sheng Lin, Ruobing Han, Chenyan Jiang, Qiwen Fang, Dechuan Kong, Yiyi Zhu, Yaxu Zheng, Xiaohuan Gong, Wenjia Xiao, Shenghua Mao, Bihong Jin, Huanyu Wu, Chen Fu
Transboundary and Emerging Diseases.2020; 67(4): 1697. CrossRef - COVID-19 pandemic—a focused review for clinicians
M. Cevik, C.G.G. Bamford, A. Ho
Clinical Microbiology and Infection.2020; 26(7): 842. CrossRef - Commentary on COVID-19 and African Americans. The Numbers are Just a Tip of a Bigger Iceberg
Cindy Ogolla Jean-Baptiste, Tyeastia Green
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics and diagnosis rate of 5630 subjects receiving SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid tests from Wuhan, China
Na Shen, Yaowu Zhu, Xiong Wang, Jing Peng, Weiyong Liu, Feng Wang, Yanjun Lu, Liming Cheng, Ziyong Sun
JCI Insight.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 in Adolescents and Young Adults
Jiaqiang Liao, Shibing Fan, Jing Chen, Jianglin Wu, Shunqing Xu, Yuming Guo, Chunhui Li, Xianxiang Zhang, Chuansha Wu, Huaming Mou, Chenxi Song, Feng Li, Guicheng Wu, Jingjing Zhang, Lian Guo, Huawen Liu, Jinglong Lv, Lixin Xu, Chunhui Lang
The Innovation.2020; 1(1): 100001. CrossRef - A case series describing the epidemiology and clinical characteristics of COVID-19 infection in Jilin Province
Na Du, Haiying Chen, Qing Zhang, Lihe Che, Lixin Lou, Xiaohua Li, Kaiyu Zhang, Wanguo Bao
Virulence.2020; 11(1): 482. CrossRef - New Insights of Emerging SARS-CoV-2: Epidemiology, Etiology, Clinical Features, Clinical Treatment, and Prevention
Gangqiang Guo, Lele Ye, Kan Pan, Yu Chen, Dong Xing, Kejing Yan, Zhiyuan Chen, Ning Ding, Wenshu Li, Hong Huang, Lifang Zhang, Xiaokun Li, Xiangyang Xue
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A novel IDEA: The impact of serial interval on a modified-Incidence Decay and Exponential Adjustment (m-IDEA) model for projections of daily COVID-19 cases
Ben A. Smith
Infectious Disease Modelling.2020; 5: 346. CrossRef - First Mildly Ill, Nonhospitalized Case of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Without Viral Transmission in the United States—Maricopa County, Arizona, 2020
Sarah E Scott, Karen Zabel, Jennifer Collins, Katherine C Hobbs, Melissa J Kretschmer, Mitchell Lach, Katie Turnbow, Lindsay Speck, Jessica R White, Keila Maldonado, Brandon Howard, Jeanene Fowler, Sonia Singh, Susan Robinson, Alexandra Peterson Pompa, Ke
Clinical Infectious Diseases.2020; 71(15): 807. CrossRef - School Opening Delay Effect on Transmission Dynamics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Korea: Based on Mathematical Modeling and Simulation Study
Soyoung Kim, Yae-Jean Kim, Kyong Ran Peck, Eunok Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Case fatality rate analysis of Italian COVID‐19 outbreak
Giovanni Giangreco
Journal of Medical Virology.2020; 92(7): 919. CrossRef - Sociodemographic, clinical and laboratory factors on admission associated with COVID-19 mortality in hospitalized patients: A retrospective observational study
Mario Rivera-Izquierdo, María del Carmen Valero-Ubierna, Juan Luis R-delAmo, Miguel Ángel Fernández-García, Silvia Martínez-Diz, Arezu Tahery-Mahmoud, Marta Rodríguez-Camacho, Ana Belén Gámiz-Molina, Nicolás Barba-Gyengo, Pablo Gámez-Baeza, Celia Cabrero-
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(6): e0235107. CrossRef - Propuesta del modelo para control de infecciones en la consulta odontológica ante la pandemia de COVID-19.
Laura María Díaz Guzmán, José L Castellanos Suárez
Revista de la Asociación Dental Mexicana.2020; 77(3): 137. CrossRef - Why lockdown? Why national unity? Why global solidarity? Simplified arithmetic tools for decision-makers, health professionals, journalists and the general public to explore containment options for the 2019 novel coronavirus
Gerry F. Killeen, Samson S. Kiware
Infectious Disease Modelling.2020; 5: 442. CrossRef - Incubation period of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Busan, South Korea
Hansol Lee, Kyungtae Kim, Kwonkyu Choi, Sangbum Hong, Hyunjin Son, Sukhyun Ryu
Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy.2020; 26(9): 1011. CrossRef - Global trends of clinical presentation of COVID-19
Ragini Sharma, MradulK Daga, Govind Mawari, VijayKumar Karra, Naresh Kumar, ManishKumar Jha, Suresh Kumar
Indian Journal of Medical Specialities.2020; 11(2): 59. CrossRef - Epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Malahat Khalili, Mohammad Karamouzian, Naser Nasiri, Sara Javadi, Ali Mirzazadeh, Hamid Sharifi
Epidemiology and Infection.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of a familial cluster of COVID-19
Yong Sun, Lin Tian, Xiaomei Du, Hua Wang, Yueshan Li, Rangbing Wu
Epidemiology and Infection.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Performance of the Luminex NxTAG CoV Extended Panel for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Nasopharyngeal Specimens from COVID-19 Patients in Hong Kong
Jonathan Hon-Kwan Chen, Cyril Chik-Yan Yip, Jasper Fuk-Woo Chan, Rosana Wing-Shan Poon, Kelvin Kai-Wang To, Kwok-Hung Chan, Vincent Chi-Chung Cheng, Kwok-Yung Yuen, Alexander J. McAdam
Journal of Clinical Microbiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection of SARS-CoV-2 by Use of the Cepheid Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 and Roche cobas SARS-CoV-2 Assays
Angelica Moran, Kathleen G. Beavis, Scott M. Matushek, Carol Ciaglia, Nina Francois, Vera Tesic, Nedra Love, Alexander J. McAdam
Journal of Clinical Microbiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evidence for transmission of COVID-19 prior to symptom onset
Lauren C Tindale, Jessica E Stockdale, Michelle Coombe, Emma S Garlock, Wing Yin Venus Lau, Manu Saraswat, Louxin Zhang, Dongxuan Chen, Jacco Wallinga, Caroline Colijn
eLife.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic serial interval as a novel indicator for contact tracing effectiveness exemplified with the SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 outbreak in South Korea
Sofia K. Mettler, Jihoo Kim, Marloes H. Maathuis
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2020; 99: 346. CrossRef - Epidemiological Characteristics of COVID-19 Outbreak at Fitness Centers in Cheonan, Korea
Sanghyuk Bae, Hwami Kim, Tae-Young Jung, Ji-Ae Lim, Da-Hye Jo, Gi-Seok Kang, Seung-Hee Jeong, Dong-Kwon Choi, Hye-Jin Kim, Young Hee Cheon, Min-kyo Chun, Miyoung Kim, Siwon Choi, Chaemin Chun, Seung Hwan Shin, Hee Kyoung Kim, Young Joon Park, Ok Park, Ho-
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Pulmonary and Extra-Pulmonary Clinical Manifestations of COVID-19
Kemmian D. Johnson, Christen Harris, John K. Cain, Cicily Hummer, Hemant Goyal, Abhilash Perisetti
Frontiers in Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Mask or no mask for COVID-19: A public health and market study
Tom Li, Yan Liu, Man Li, Xiaoning Qian, Susie Y. Dai, Kednapa Thavorn
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(8): e0237691. CrossRef - COVID-19 induced liver function abnormality associates with age
Shasha Li, Jinsong Li, Zhenhua Zhang, Lin Tan, Tuo Shao, Ming Li, Xiuyong Li, Jacinta A. Holmes, Wenyu Lin, Mingfeng Han
Aging.2020; 12(14): 13895. CrossRef - Incubation period of COVID-19: a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis of observational research
Conor McAloon, Áine Collins, Kevin Hunt, Ann Barber, Andrew W Byrne, Francis Butler, Miriam Casey, John Griffin, Elizabeth Lane, David McEvoy, Patrick Wall, Martin Green, Luke O'Grady, Simon J More
BMJ Open.2020; 10(8): e039652. CrossRef - Lessons from the Mainland of China’s Epidemic Experience in the First Phase about the Growth Rules of Infected and Recovered Cases of COVID-19 Worldwide
Chuanliang Han, Yimeng Liu, Jiting Tang, Yuyao Zhu, Carlo Jaeger, Saini Yang
International Journal of Disaster Risk Science.2020; 11(4): 497. CrossRef - China’s practice to prevent and control COVID-19 in the context of large population movement
Tie-Long Xu, Mei-Ying Ao, Xu Zhou, Wei-Feng Zhu, He-Yun Nie, Jian-He Fang, Xin Sun, Bin Zheng, Xiao-Fan Chen
Infectious Diseases of Poverty.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Lung Mechanics of Mechanically Ventilated Patients With COVID-19: Analytics With High-Granularity Ventilator Waveform Data
Huiqing Ge, Qing Pan, Yong Zhou, Peifeng Xu, Lingwei Zhang, Junli Zhang, Jun Yi, Changming Yang, Yuhan Zhou, Limin Liu, Zhongheng Zhang
Frontiers in Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Research on COVID-19: A Bibliometric Analysis
Yue Gong, Ting-can Ma, Yang-yang Xu, Rui Yang, Lan-jun Gao, Si-hua Wu, Jing Li, Ming-liang Yue, Hui-gang Liang, Xiao He, Tao Yun
The Innovation.2020; 1(2): 100027. CrossRef - Modeling the Prevalence of Asymptomatic COVID-19 Infections in the Chinese Mainland
Xiaoqian Jia, Junxi Chen, Liangjing Li, Na Jia, Bahabaike Jiangtulu, Tao Xue, Le Zhang, Zhiwen Li, Rongwei Ye, Bin Wang
The Innovation.2020; 1(2): 100026. CrossRef - COVID-19 in Nursing Facilities: Experience in Republic of Korea
Rok Song, Hee-Sook Kim, Seok-Ju Yoo, Kwan Lee, Ji-Hyuk Park, Joon Ho Jang, Gyoung-Sook Ahn, Jun-Nyun Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2020; 11(4): 164. CrossRef - Estimating the Effectiveness of Non-pharmaceutical Interventions on COVID-19 Control in Korea
Kyung-Duk Min, Heewon Kang, Ju-Yeun Lee, Seonghee Jeon, Sung-il Cho
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The transmission modes and sources of COVID-19: A systematic review
Heshu Sulaiman Rahman, Masrur Sleman Aziz, Ridha Hassan Hussein, Hemn Hassan Othman, Shirwan Hama Salih Omer, Eman Star Khalid, Nusayba Abdulrazaq Abdulrahman, Kawa Amin, Rasedee Abdullah
International Journal of Surgery Open.2020; 26: 125. CrossRef - The impact of social distancing and public behavior changes on COVID-19 transmission dynamics in the Republic of Korea
Soyoung Kim, Youngsuk Ko, Yae-Jean Kim, Eunok Jung, Yury E. Khudyakov
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(9): e0238684. CrossRef - Coronavirus, la epidemia que cambió el mundo
Leonardo López Almejo, Luis Gerardo Padilla Rojas, Darío Esaú Garín Zertuche, Michael Dittmar Johnson
Ortho-tips.2020; 16(2): 54. CrossRef - Laboratory Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 19 (COVID-19) in Korea: Current Status, Limitation, and Challenges
Gi Seon Song, You-Rim Lee, Sungmin Kim, Wontae Kim, Jungwon Choi, Dahyeon Yoo, Jungyoung Yoo, Kyung-Tae Jang, Jaewang Lee, Jin Hyun Jun
The Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2020; 52(3): 284. CrossRef - Response to COVID-19 in South Korea and implications for lifting stringent interventions
Amy Dighe, Lorenzo Cattarino, Gina Cuomo-Dannenburg, Janetta Skarp, Natsuko Imai, Sangeeta Bhatia, Katy A. M. Gaythorpe, Kylie E. C. Ainslie, Marc Baguelin, Samir Bhatt, Adhiratha Boonyasiri, Nicholas F. Brazeau, Laura V. Cooper, Helen Coupland, Zulma Cuc
BMC Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Incubation Period of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Novel Coronavirus 2 that Causes Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Gizachew Tadesse Wassie, Abebaw Gedef Azene, Getasew Mulat Bantie, Getenet Dessie, Abiba Mihret Aragaw
Current Therapeutic Research.2020; 93: 100607. CrossRef - Definition and retrospective application of a clinical scoring system for COVID-19 triage at presentation
Jun Duan, Mei Liang, Yongpu Li, Dan Wu, Ying Chen, Shui Gao, Ping Jia, Mei Yang, Wei Xia, Xiaolan Wu, Quan Li, Fulin Zuo, Yahong Zhang, Yongfang He, Jianghua Nie, Wenxiu Zhou, Xueqin Fu, Xiaobin Peng, Zhoujun Ma, Xiaofeng Fu, Lingwei Zeng, Wenyi You, Yuan
Therapeutic Advances in Respiratory Disease.2020; 14: 175346662096301. CrossRef - Early epidemiological indicators, outcomes, and interventions of COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review
Urvish Patel, Preeti Malik, Deep Mehta, Dhaivat Shah, Raveena Kelkar, Candida Pinto, Maria Suprun, Mandip Dhamoon, Nils Hennig, Henry Sacks
Journal of Global Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Hospital admission rates, length of stay, and in-hospital mortality for common acute care conditions in COVID-19 vs. pre-COVID-19 era
A.A. Butt, A.B. Kartha, N.A. Masoodi, A.M. Azad, N.A. Asaad, M.U. Alhomsi, H.A.H. Saleh, R. Bertollini, A.-B. Abou-Samra
Public Health.2020; 189: 6. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 y RT-PCR en pacientes asintomáticos: resultados de una cohorte de trabajadores del Aeropuerto Internacional El Dorado de Bogotá, 2020
Jeadran Malagón-Rojas, Claudia Gómez-Rendón , Eliana L. Parra , Julia Almentero , Ruth Palma , Ronald López , Yesith Guillermo Toloza-Pérez , Vivian Rubio , Juan Felipe Bedoya , Fernando López-Díaz , Carlos Franco-Muñoz , Jhonnatan Reales-Gonzá
Biomédica.2020; 40(Supl. 2): 166. CrossRef - Transmissibility of coronavirus disease 2019 in Chinese cities with different dynamics of imported cases
Ka Chun Chong, Wei Cheng, Shi Zhao, Feng Ling, Kirran N. Mohammad, Maggie Wang, Benny CY Zee, Lai Wei, Xi Xiong, Hengyan Liu, Jingxuan Wang, Enfu Chen
PeerJ.2020; 8: e10350. CrossRef - Compositional cyber-physical epidemiology of COVID-19
Jin Woo Ro, Nathan Allen, Weiwei Ai, Debi Prasad, Partha S. Roop
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Reproductive number of coronavirus: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on global level evidence
Md. Arif Billah, Md. Mamun Miah, Md. Nuruzzaman Khan, Maria Elena Flacco
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0242128. CrossRef - Evidence of Long-Distance Droplet Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 by Direct Air Flow in a Restaurant in Korea
Keun-Sang Kwon, Jung-Im Park, Young Joon Park, Don-Myung Jung, Ki-Wahn Ryu, Ju-Hyung Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Rapid review of available evidence on the serial interval and generation
time of COVID-19
John Griffin, Miriam Casey, Áine Collins, Kevin Hunt, David McEvoy, Andrew Byrne, Conor McAloon, Ann Barber, Elizabeth Ann Lane, SImon More
BMJ Open.2020; 10(11): e040263. CrossRef - Ten Epidemiological Parameters of COVID-19: Use of Rapid Literature Review to Inform Predictive Models During the Pandemic
Luciana Guerra Gallo, Ana Flávia de Morais Oliveira, Amanda Amaral Abrahão, Leticia Assad Maia Sandoval, Yure Rodrigues Araújo Martins, Maria Almirón, Fabiana Sherine Ganem dos Santos, Wildo Navegantes Araújo, Maria Regina Fernandes de Oliveira, Henry Mai
Frontiers in Public Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): The Singapore Experience. A Review of the First Eight Months
Trevor Hwee Yong Tan, Matthias Paul Han Sim Toh, Shawn Vasoo, David Chien Boon Lye, Brenda Sze Peng Ang, Yee Sin Leo, Vernon Jian Ming Lee, Ser Hon Puah, Asok Kurup
Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.2020; 49(10): 764. CrossRef - Keeping Low Reproductive Number Despite the Rebound Population Mobility in Korea, a Country Never under Lockdown during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Soyoung Kim, Yae-Jean Kim, Kyong Ran Peck, Youngsuk Ko, Jonggul Lee, Eunok Jung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(24): 9551. CrossRef - Operating a National Hotline in Korea During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Rok Song, Yuh Seog Choi, Jae Young Ko
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2020; 11(6): 380. CrossRef - Using Automated-Machine Learning to Predict COVID-19 Patient Mortality (Preprint)
Kenji Ikemura, Eran Bellin, Yukako Yagi, Henny Billett, Mahmoud Saada, Katelyn Simone, Lindsay Stahl, James Szymanski, D.Y. Goldstein, Morayma Reyes Gil
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - El desafío de los portadores asintomáticos de COVID-19: una revisión rápida de la literatura
Cidronio Albavera-Hernández, Jorge Martin Rodríguez-Hernández, Flor Stella Piñeros-Garzón, Sandra Milena Montoya-Sanabria
Revista de Salud Pública.2020; 22(6): 1. CrossRef - Global Cities and Socioeconomic Inequality: A Pathways Inquiry
Herman L. Boschken
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The agreed experts’ position of the Eurasian Association of Therapists on tactics of management of patients with comorbid pathology infected with SARS-Cov-2
G. P. Arutiunov, E. I. Tarlovskaia, N. A. Koziolova, M. V. Boldina, M. M. Batiushin, A. S. Ametov, A. G. Arutiunov, A. S. Belevskii, G. R. Galstian, N. I. Grigor’eva, G. A. Dzhunusbekova, A. M. Esaian, S. V. Mal’chikova, N. P. Mit’kovskaia, A. M. Mkrtumia
Terapevticheskii arkhiv.2020; 92(9): 108. CrossRef - Digitalisation and COVID-19: The Perfect Storm
Denis Horgan, Joanne Hackett, C. Benedikt Westphalen, Dipak Kalra, Etienne Richer, Mario Romao, Antonio L. Andreu, Jonathan A. Lal, Chiara Bernini, Birute Tumiene, Stefania Boccia, Antoni Montserrat
Biomedicine Hub.2020; 5(3): 1. CrossRef - ROLE OF TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS IN CORONAVIRUS INFECTION AND IMMUNE RESPONSE
Muhammad Sarfaraz Iqbal, Nimra Sardar, Wajiha Akmal, Rabia Sultan, Humaira Abdullah, Maimoona Qindeel, Kuldeep Dhama, Muhammad Bilal
Journal of Experimental Biology and Agricultural Sciences.2020; 8(Spl-1-SARS): S66. CrossRef - Literature Review of Epidemiological Phenomena: Corona Virus Disease Pandemic 2019
Yarmaliza Yarmaliza, Teungku Nih Farisni, Fitriani Fitriani, Zakiyuddin Zakiyuddin, Fitrah Reynaldi, Safrizal Safrizal, Lili Eky Nursia N
European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences.2020;[Epub] CrossRef

 KSE
KSE
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite